Communication Manager Maintenance-Object Repair Procedures
1406 Maintenance Procedures for Avaya Communication Manager 3.0, Media Gateways and Servers
The active media server’s maintenance software is responsible for maintaining the SOH of both
the active and standby IPSI in each PN. If an active IPSI’s SOH is lower than the standby’s, IPSI
interchange is initiated. The following list contains failures and actions that cause an
interchange:
Active IPSI has a faulty Tone-Clock.
1. IPSI’s hardware detects loss of clock, and its firmware initiates clock interchange.
2. IPSI’s firmware notifies software of loss of clock.
3. Software interchanges Archangel.
4. Software interchanges PKT-INT.
5. The port-network is COLD started.
Active IPSI has a faulty PKT-INT.
1. Software detects faulty PKT-INT.
2. Software interchanges PKT-INT.
3. Software interchanges Archangel.
4. Software interchanges Tone-Clock.
Active IPSI has a faulty Archangel.
1. PKT-INT detects dead EAL and reports it to software.
2. Software interchanges Tone-Clock.
3. Software interchanges Archangel.
4. Software interchanges PKT-INT.
Both IPSIs are healthy (planned interchange sequence).
1. Software interchanges Tone-Clock.
2. Software interchanges Archangel.
3. Software interchanges PKT-INT.
If both of a PN’s IPSIs have faulty Tone-Clock, then the PN is out of service.
If both of a PN’s IPSIs have faulty EAL and/or PKT-INT, then the PN “falls back” to EI-EAL mode
of operation, where:
● The PN’s Expansion Interface circuit pack (EI) provides Archangel functionality
● Another PN’s IPSI provides PKT-INT functionality
For details, see EXP-INTF (Expansion Interface Circuit Pack)
on page 1176.
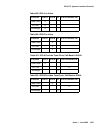
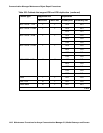
Table 499: IPSI A is Active
on page 1407, Table 500: IPSI B is Active on page 1407,
Table 501: IPSI A Provides Tone-Clock; Fall-Back to EI-EAL
on page 1407, and
Table 502: IPSI B Provides Tone-Clock; Fall-Back to EI-EAL
on page 1407 show the valid
combinations of IPSIs and EIs providing Tone-Clock, PKT-INT, and Archangel functions.