Event Data
Issue 1 June 2005 129
2. Convert the hexadecimal number provided in Event Data 2 to three binary numbers: put a
one in the appropriate binary number positions that add up to the value of the number.
Each binary number consists of eight bits. See Table 40: Event Data 2 conversion
example on page 129 for an example of the hexadecimal number 0x429, and
Table 41: Hexadecimal, decimal, and binary equivalents
on page 130 for the binary
equivalents for individual digits.
3. Add up the decimal weights that have a one for each of the eight bit segments.
● Convert Cause Value 0x29 to decimal and find the sum.
Cause Value (Bits 1 - 8): 1 +8 + 32 = 41. This is Cause Value 41.
● Convert Location Code 0x4 to decimal and find the sum.
Location Code (Bits 9 - 16): 4 = 4. This is Location Code 4.
● Convert Diagnostic Value 0x00 (Bits 17 - 24): 0 = 0.
Diagnostic Code is 0, not provided for this example denial event.
4. Use the information in this chapter to find an explanation of the Data Event 2 information.
● Cause Value 41 = Temporary Failure. See Cause Values on page 134.
● Location Code 4 = Remote Network/Public Network Serving Remote User (the Local
Exchange Carrier at the far end of the call). See Table 42: Location Code definitions
on
page 130.
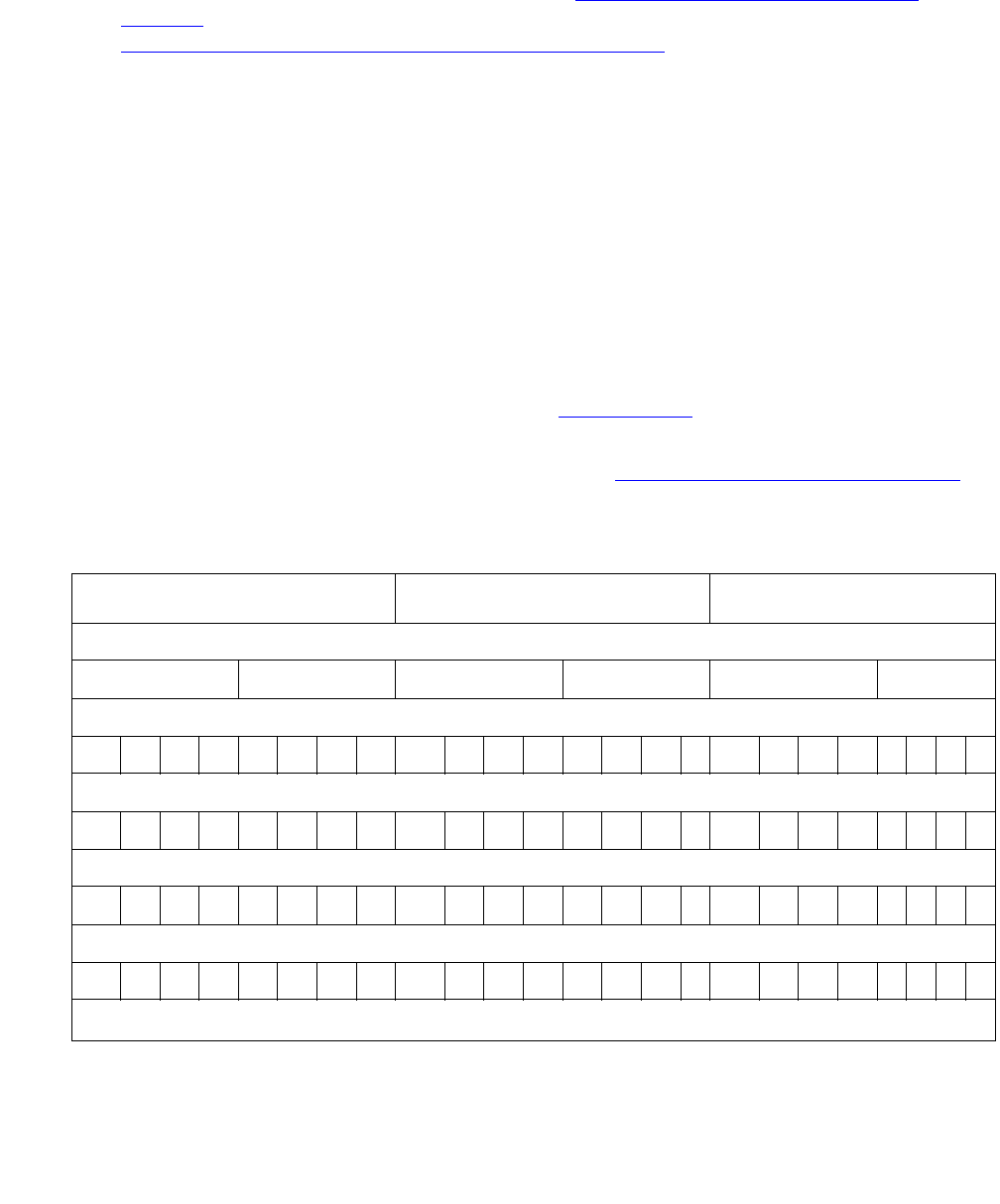
Table 40: Event Data 2 conversion example
Diagnostic Code Location Code Cause Value
Event Data 2
000429
Binary number
00000000 00001000 0101001
Decimal weight of each digit position
8 42184218 42184218 4218421
Decimal weight of the binary positions for each eight-bit field
128643216842112864321684211286432168421
Bit position
24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1


















