1 - 20
Chapter 1 Product Outline
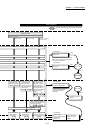
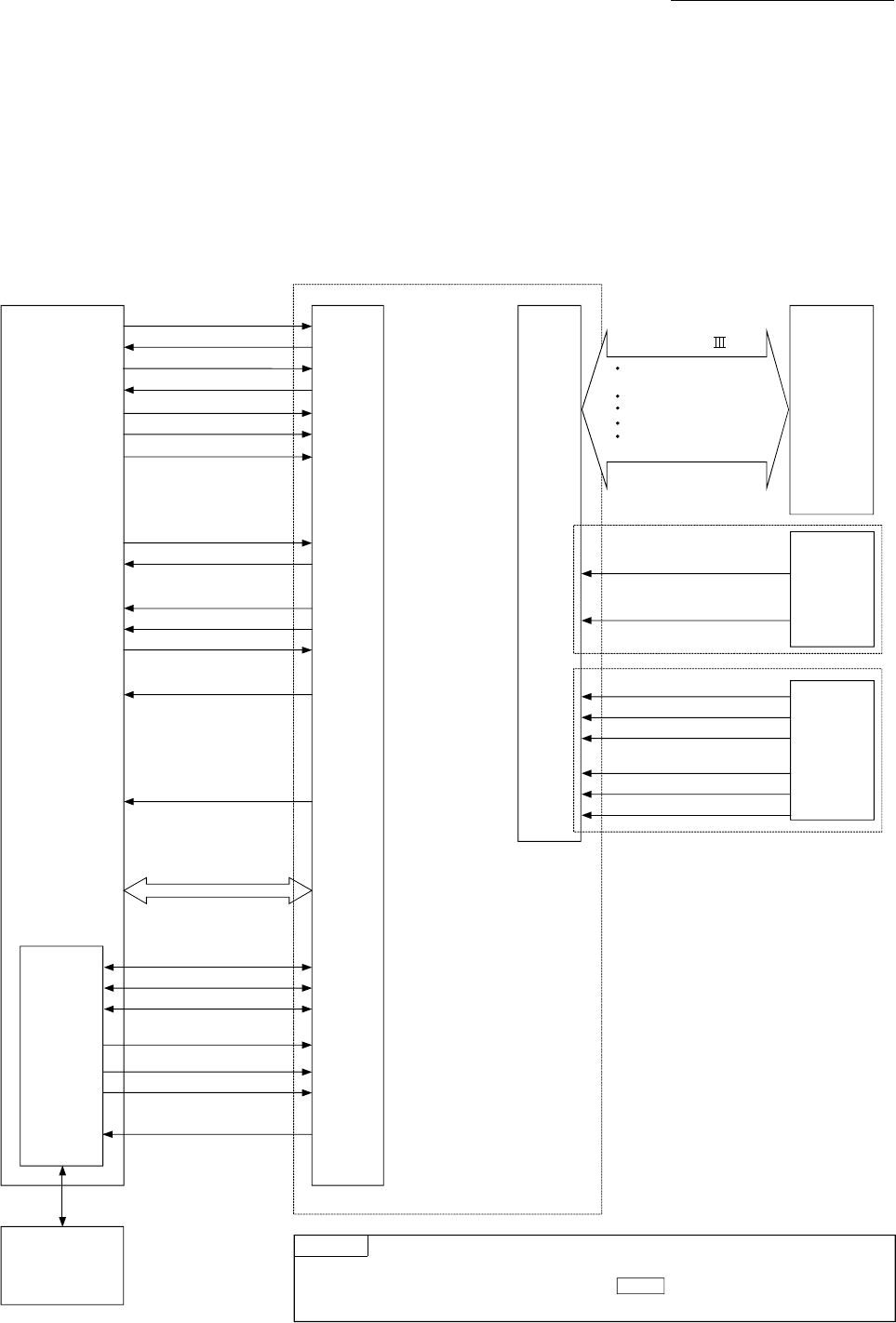
1.1.6 Communicating signals between QD77MS and each module
The outline of the signal communication between the Simple Motion module and PLC
CPU, GX Works2 and servo amplifier, etc., is shown below.
(GX Works2 communicates with the Simple Motion module via the PLC CPU to which
it is connected.)
(1) QD77MS2/QD77MS4
READY signal
Forward run JOG start signal
Positioning start signal
BUSY signal
Axis stop signal
Start complete signal
Error detection signal
Servo
amplifier
QD77MS2/QD77MS4
Y0
Y10,Y11,Y12,Y13
X0
Y8,YA,YC,YE
PLC CPU
Manual pulse
generator/
Incremental
synchronous
encoder
Operation monitor
Parameter write/read
JOG operation, inching operation
(Test)
Positioning operation (Test)
OPR operation (Test)
GX Works2
Peripheral
device
interface
Y9,YB,YD,YF
X14,X15,X16,X17
XC,XD,XE,XF
X10,X11,X12,X13
Y4,Y5,Y6,Y7
X4,X5,X6,X7
X8,X9,XA,XB
Synchronization flag
X1
Execution prohibition flag
Y14,Y15,Y16,Y17
All axis servo ON signal
Y1
Reverse run JOG start signal
Positioning complete signal
M code ON signal
Interface
with
PLC CPU
External
interface
PLC READY signal
Data write/read
Positioning data write/read
Block start data write/read
Operating information of
the servo amplifier
Positioning command
Control command
Servo parameter
External input signal of
the servo amplifier
SSCNET (/H)
Manual pulse generator/
Incremental synchronous encoder
A-phase
Manual pulse generator/
Incremental synchronous encoder
B-phase
POINT
When using the upper/lower limit signal, stop signal, near-point dog signal of the external
input signal via CPU, use the buffer memory in " External input signal operation
device".
Cd.44
Forced stop input signal
External command signal/
Switching signal
External
input signal
Upper limit signal
Lower limit signal
STOP signal
Near-point dog signal