8 - 11
Chapter 8 OPR Control
8.2.5 OPR method (3): Count method 2)
The following shows an operation outline of the OPR method "count method 2)".
The "count method 2)" method is effective when a "zero signal" cannot be received.
(Note that compared to the "count method 1)" method, using this method will result in
more deviation in the stop position during machine OPR.)
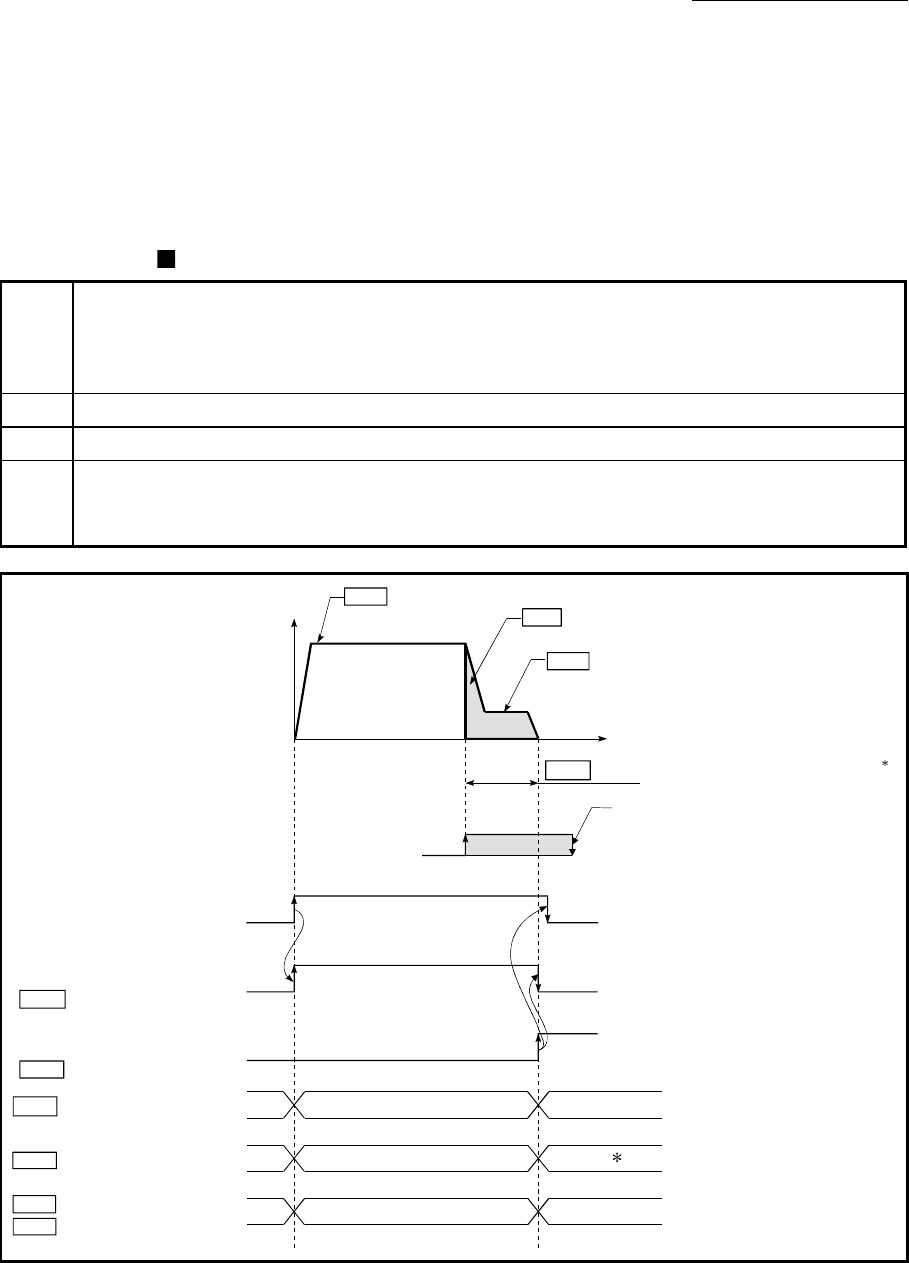
Operation chart
1)
The machine OPR is started.
(The machine begins the acceleration designated in "[Pr.51] OPR acceleration time selection", in the
direction designated in "[Pr.44] OPR direction". It then moves at the "[Pr.46] OPR speed" when the
acceleration is completed.)
2)
The machine begins decelerating when the near-point dog ON is detected.
3)
The machine decelerates to the "[Pr.47] Creep speed", and subsequently moves at that speed.
4)
The command from the Simple Motion module will stop and the machine OPR will be completed when the
machine moves the movement amount set in "[Pr.50] Setting for the movement amount after near-point
dog ON" from the near-point dog ON position.
Md.21 Machine feed value
t
V
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
0
OFF
Pr. 46 OPR speed
Pr. 47 Creep speed
Pr.50 Setting for the movement amount
after near-point dog ON
Md.34 Movement amount after near-point dog ON
Leave sufficient distance from the home
position to the near-point dog OFF.
Machine OPR start
(Positioning start signal)
OPR
Inconsistent
Value the machine moved is stored
Inconsistent
Md.34 Movement amount
after near-point dog ON
Md.20 Current feed value
Md.26 Axis operation status
Standby Standby
Value of .
OP address
OPR request flag
( Md.31 Status : b3)
OPR complete flag
( Md.31 Status : b4)
1
Near-point dog
1
Fig. 8.7 Count method 2) machine OPR