5 - 23
Chapter 5 Data Used for Positioning Control
[Pr.1] Unit setting
Set the unit used for defining positioning operations. Choose from the following
units depending on the type of the control target: mm, inch, degree, or PLS.
Different units can be defined for different axes.
(Example) Different units (mm, inch, degree, and PLS) are applicable to different
systems:
• mm or inch...... X-Y table, conveyor (Select mm or inch depending on
the machine specifications.)
• degree ............ Rotating body (360 degrees/rotation)
• PLS ................. X-Y table, conveyor
: When you change the unit, note that the values of other parameters and data
will not be changed automatically.
After changing the unit, check if the parameter and data values are within the
allowable range.
Set "degree" to exercise speed-position switching control (ABS mode).
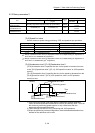
[Pr.2] to [Pr.4] Electronic gear (Movement amount per pulse)
Mechanical system value used when the Simple Motion module performs
positioning control.
The settings are made using [Pr.2] to [Pr.4].
The electronic gear is expressed by the following equation.
Electronic gear =
Number of pulses per rotation (AP)
Movement amount per rotation (AL)
Unit magnification (AM)
: When positioning has been performed, an error (mechanical system error) may
be produced between the specified movement amount and the actual
movement amount. (Refer to Section 13.3.2 "Electronic gear function".)