17. APPLICATION OF FUNCTIONS
17 - 60
(1) Summary
The master-slave operation function transmits a master axis torque to slave axes using driver
communication and the torque as a command drives slave axes by torque control.
Transmission of torque data from the master axis to slave axes is via SSCNET III/H. Additional wiring is
not required.
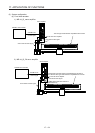
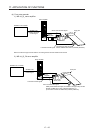
(2) System configuration
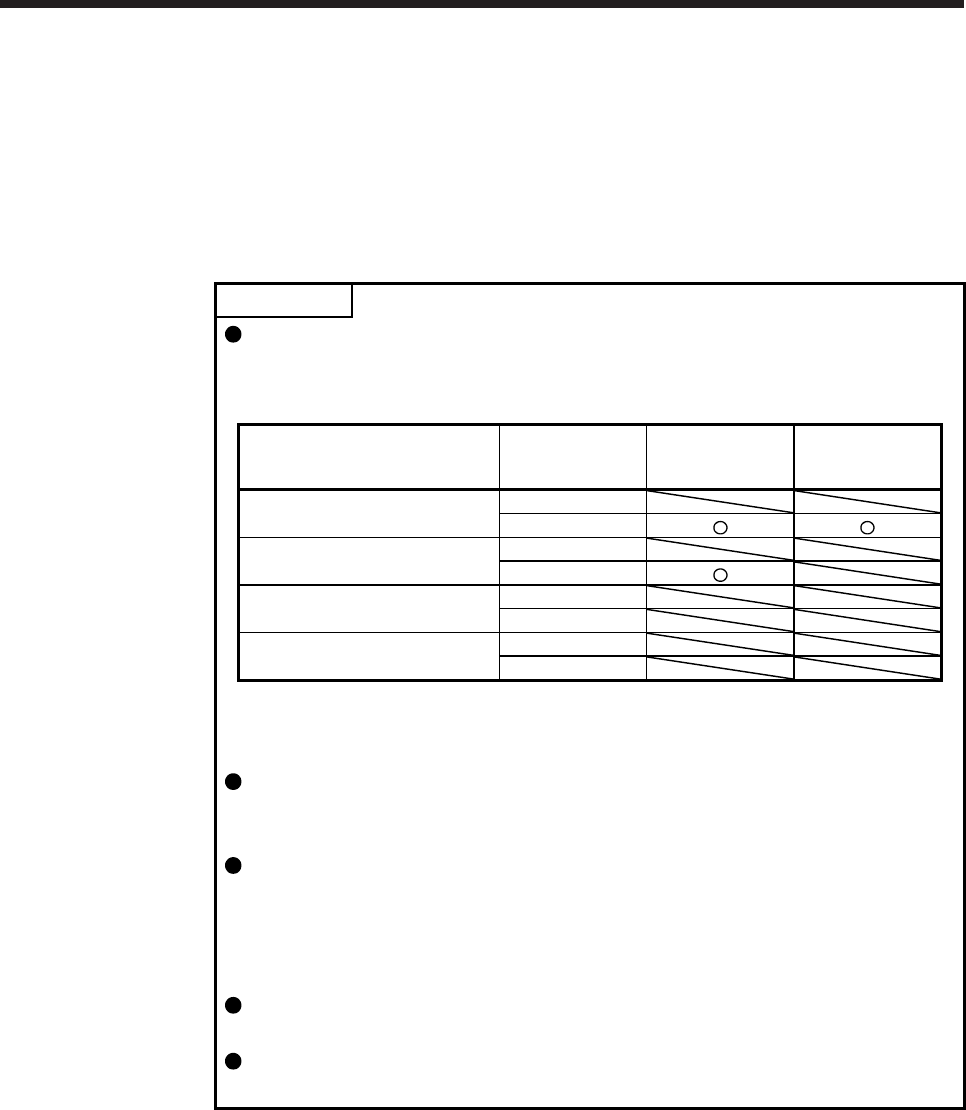
POINT
The control modes compatible with the master-slave operation function are as
follows.
Master-slave operation function compatibility table
Control mode
Forced stop
deceleration
function
Master axis (Note) Slave axis (Note)
Standard control mode
Enabled
Disabled
Fully closed loop control mode
Enabled
Disabled
Linear servo motor control mode
Enabled
Disabled
DD motor control mode
Enabled
Disabled
Note. When a setting for the master-slave operation is set to an axis which is not compatible with the
master-slave operation function, [AL. 37] will occur.
The master axis and slave axis are recommended to use for a linked condition
on a mechanical constitution. When they are not linked, they can reach a speed
limit level. Doing so may cause [AL. 31 Overspeed].
The slave axes use the control command from the master axis. Therefore, the
controller mainly controls parameter settings, servo-on command, acquisition of
monitor information from a servo amplifier, etc. The commands regarding
absolute positioning such as setting absolute position detection and requiring
home position setting from the controller to slave axes must not be made.
Configure the circuit so that all the master and slave axes are stopped at the
moment of a stop of a master or slave axis due to such as a servo alarm.
When the STO signal of a servo amplifier is used, the master axis and slave axis
should be turned off simultaneously.