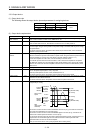
3. SIGNALS AND WIRING
3 - 34
3.8.2 Detailed explanation of interfaces
This section provides the details of the I/O signal interfaces (refer to the I/O division in the table) given in
section 3.5. Refer to this section and make connection with the external device.
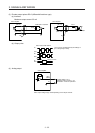
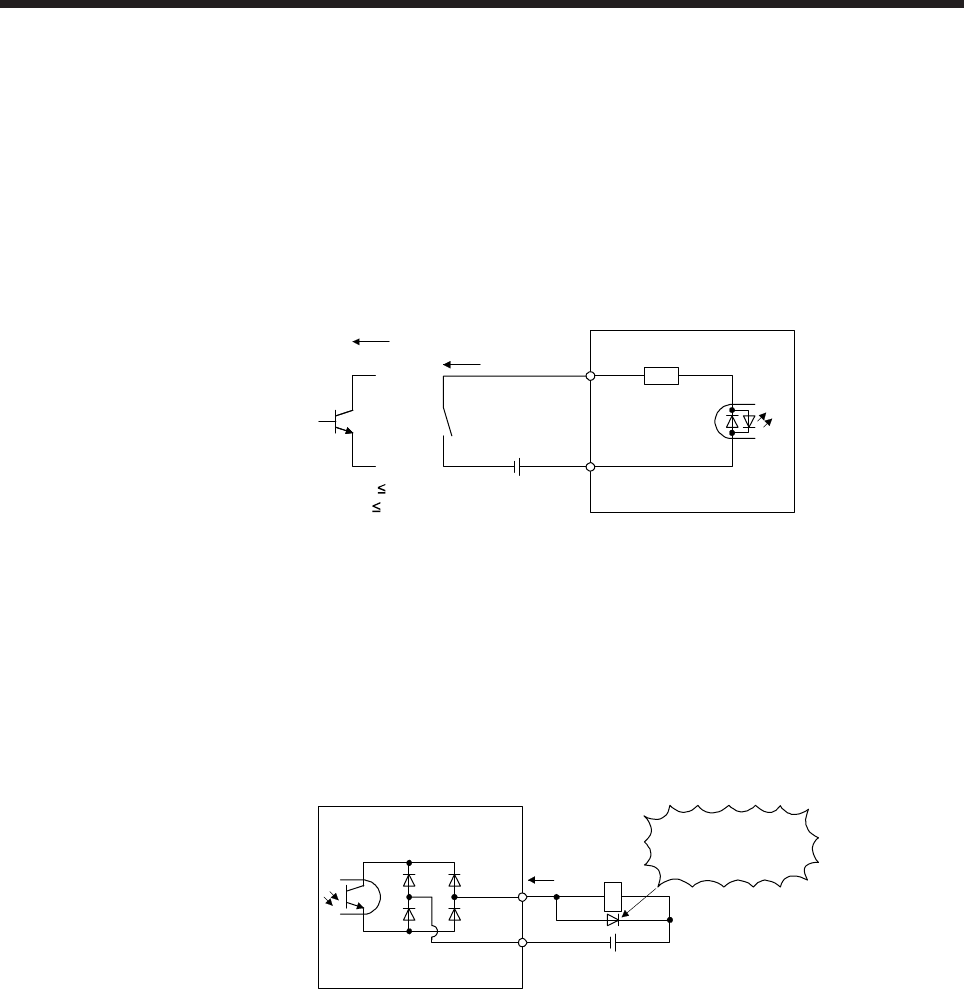
(1) Digital input interface DI-1
This is an input circuit whose photocoupler cathode side is input terminal. Transmit signals from sink
(open-collector) type transistor output, relay switch, etc. The following is a connection diagram for sink
input. Refer to section 3.8.3 for source input.
Approximately
6.2 kΩ
Approximately
5 mA
V
CES
1.0 V
I
CEO
100 µA
TR
24 V DC ± 10%
300 mA
Switch
For transistor
EM2,
etc.
Servo amplifier
DICOM
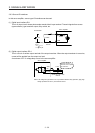
(2) Digital output interface DO-1
This is a circuit of collector output terminal of the output transistor. When the output transistor is turned
on, collector terminal current will be applied for the output.
A lamp, relay or photocoupler can be driven. Install a diode (D) for an inductive load, or install an inrush
current suppressing resistor (R) for a lamp load.
(Rated current: 40 mA or less, maximum current: 50 mA or less, inrush current: 100 mA or less) A
maximum of 2.6 V voltage drop occurs in the servo amplifier.
The following shows a connection diagram for sink output. Refer to section 3.8.3 for source output.
(Note) 24 V DC ± 10%
300 mA
If polarity of diode is
reversed, servo amplifier
will malfunction.
Servo amplifier
ALM,
etc.
Load
DOCOM
Note. If the voltage drop (maximum of 2.6 V) interferes with the relay operation, apply high
voltage (maximum of 26.4 V) from external source.