Emerson Process Management GmbH & Co. OHG 3-3
X-STREAM X2
Instruction Manual
HASX2E-IM-HS
02/2012
3
Measuring Principles
3.1 Infrared (IR) and Ultraviolet (UV) Measurement
3.1.2 NDIR Detector
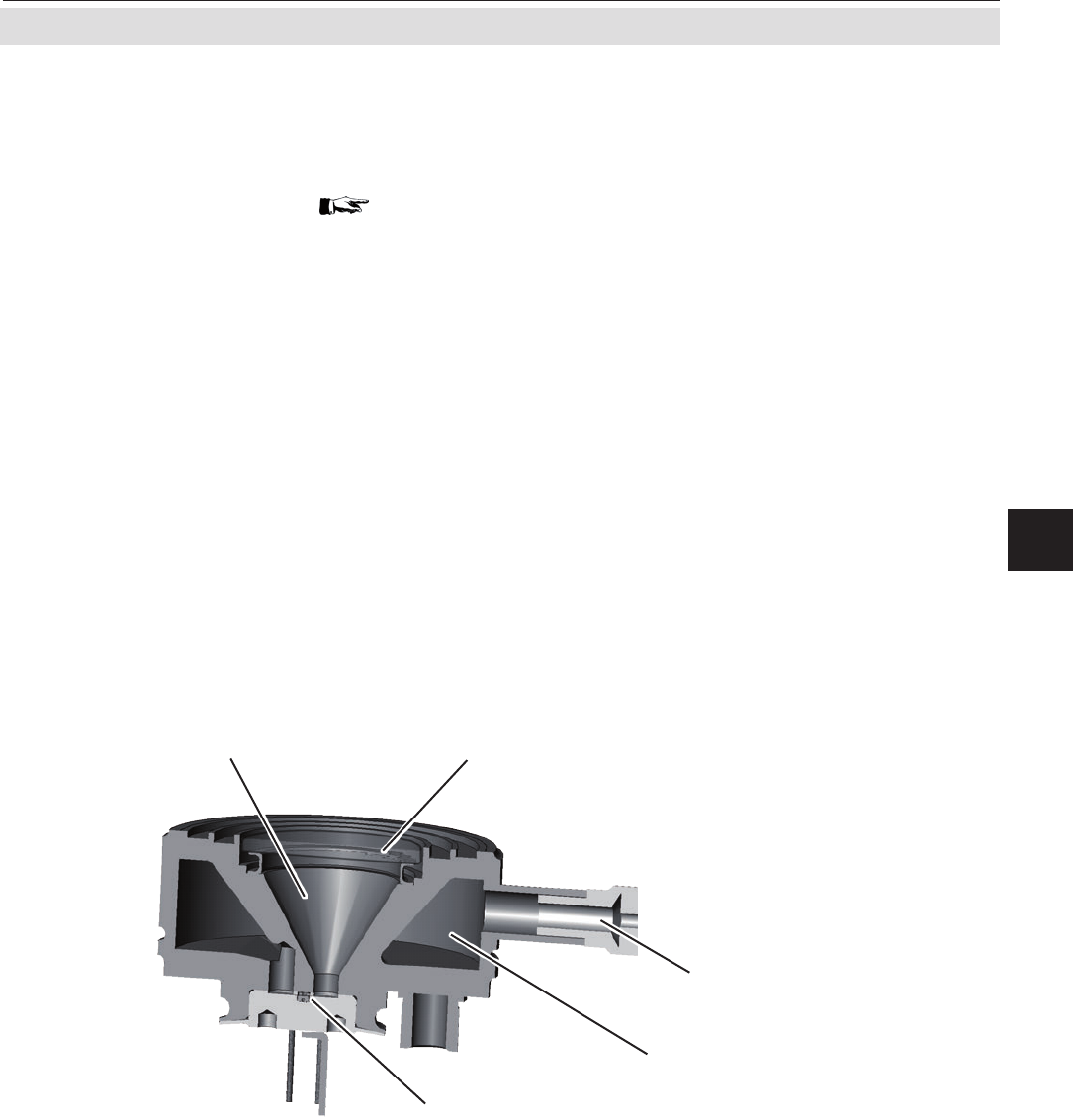
Fig. 3-2: Gas detector design principle
Compensation chamber
Fill nozzle
Absorption chamber
Connecting channel
with
micro ow detector
Window
The standard detector used for NDIR
measurements is an opto pneumatic detector.
It consists of two chambers, lled with gas and
connected via a small channel ( Fig. 3-2).
The gas lling is chosen to provide maximum
overlap with the gas to be measured. Usually
the gas to be measured itself is used.
A micro ow sensor, placed in the connecting
channel, measures the ow between both
chambers. As light is absorbed by the gas in
the absorption chamber, the gas temperature
changes. This results in an increase of volume
of the heated gas: The gas expands and ows
towards the compensation chamber. When
the chopper closes, no light is absorbed and
thus temperature and volume of the gas in
the absorption chamber decrease. Gas ows
back from the (now) hotter compensation
chamber into the absorption chamber. The
absolute ow, detected by the micro ow sen-
sor, in both cases is therefore a measure for
the light absorbed while the chopper is open.
This directly correlates to the amount of light
not absorbed in the analysis cell and therefore
to the concentration of the measurement gas
inside the analysis cell.
Using the divided analysis cell and the IntrinzX
chopper wheel, this enables simultaneous de-
tection of measurement and reference signal.