Emerson Process Management GmbH & Co. OHG 5-29
X-STREAM X2
Instruction Manual
HASX2E-IM-HS
02/2012
5
Startup
5.7 Checking the Settings
The “SpanRange” parameter is displayed in
the INFO - RANGE menu (
6.2.5.1, page
6-62) and is always given as the percentage
of
the upper range limit of the selected channel.
The “SpanRange” parameter is preset and
cannot be modied by the operator. It is used
for various functions:
Firstly, this parameter determines the maxi-
mum possible value of the span gas:
A SpanRange of e.g. 220 % means that the
greatest permitted value of the span gas for
the selected channel is 220 % of the maxi-
mum measuring range.
Example 1:
The oxygen measuring range is 10 %. If the
SpanRange is set to 220 %, the maximum
permissable span gas concentration is 22 %,
enabling to use ambient air (21 % O
2
) as a
span gas.
Furthermore, the “SpanRange” parameter
determines the range for concentration
limits. 100 percentage points are subtracted
from the value of this parameter: The result
determines by how much above or below the
measuring range limits may be set.
Example 2:
Range upper limit: 1000 ppm,
SpanRange: 100 %.
This means that the span gas range coincides
with the measuring range. Limits may not lie
outside this range: only limits betweeb 0 ppm
and 1000 ppm are admissable.
Example 4:
Range upper limit: 1000 ppm,
SpanRange: 110 %.
This means that the span gas range exceeds
the upper measuring range limit by 10 %. The
lower limit may therefore be 10 % below the
lower range limit: limits of between -100 ppm
and +1100 ppm are admissable.
Example 4:
Range upper limit: 1000 ppm,
SpanRange: 220 %.
This means that the span gas range exceeds
the measuring range by 120 % in both di-
rections (220 % - 100 % = 120 %): the limits
may be set between -1200 ppm (-120 % of
1000 ppm) and +2200 ppm (+220 % of 1000
ppm).
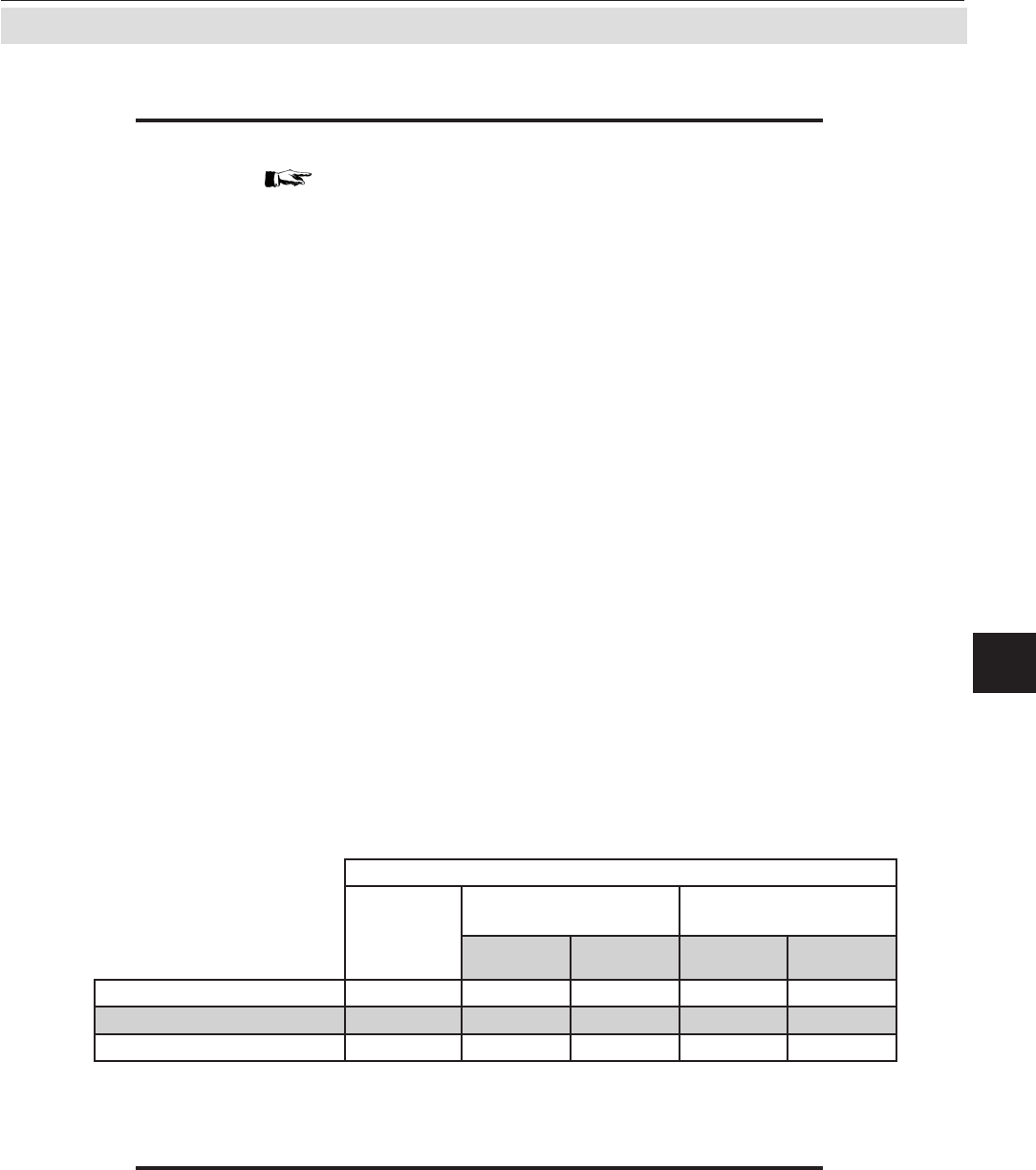
Tab. 5-3: Inuence of “SpanRange” Parameter on Concentration Alarm Limits
Range: 0 ... 1000 ppm
Parameter
"Span
range"
Span range exceeds
measuring range by
Permissible
concentration limits
relative
value
absolute
value
lower limit upper limit
Example 2 (see text) 100 % 0 % 0 ppm 0 ppm 1000 ppm
Example 3 (see text) 110 % 10 % 100 ppm -100 ppm 1100 ppm
Example 4 (see text) 220 % 120 % 1200 ppm -1200 ppm 2200 ppm


















