7 - 4
7 OPERATION CONTROL PROGRAMS
(4) How to specify data
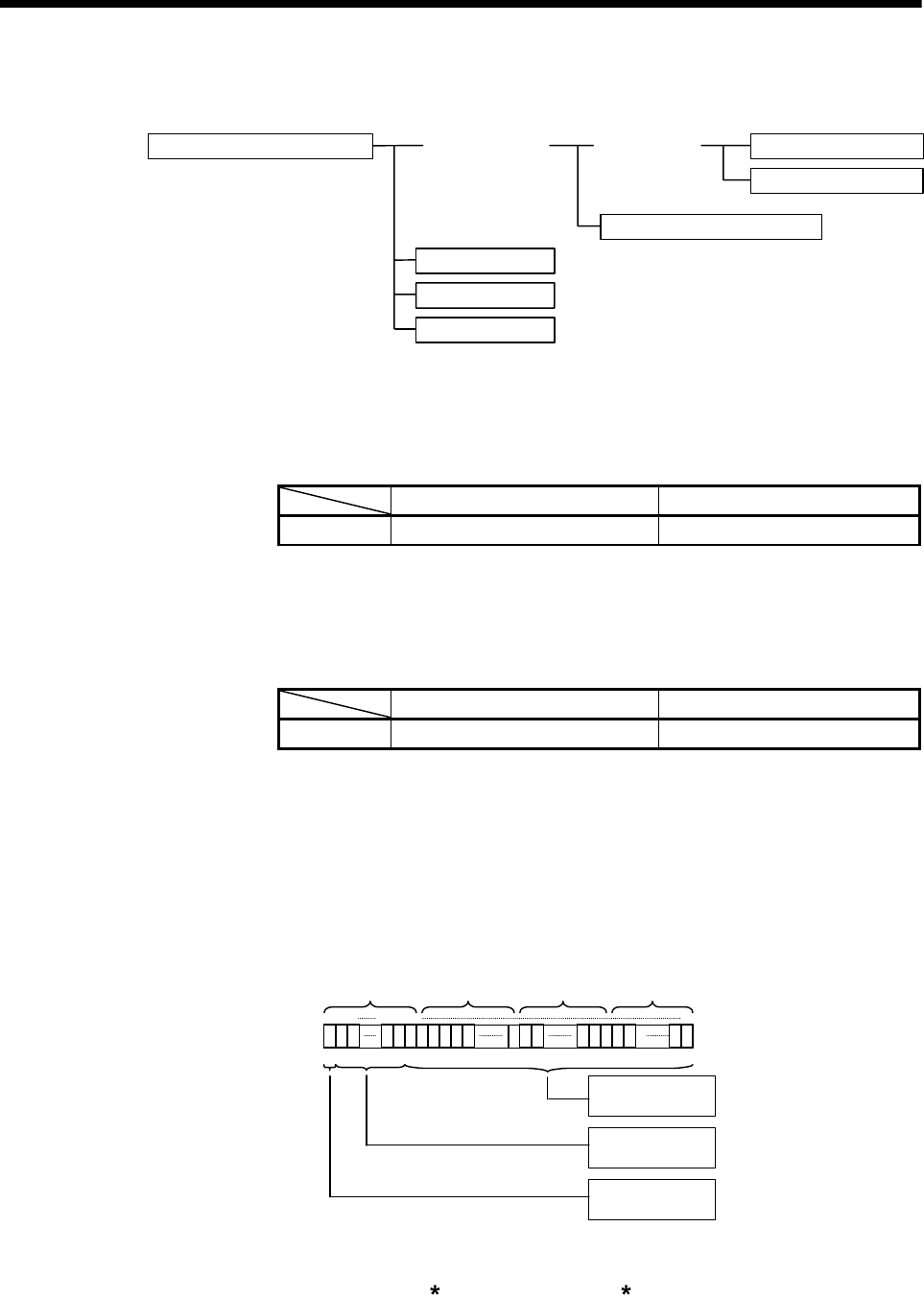
There are the following six different data usable in each instruction.
Data usable in each instruction
Bit data
Numerical data
Logical data
16-bit integer type data
32-bit integer type data
64-bit floating-point type data
Integer data
Batch bit data
(a) 16-bit integer type data
The 16-bit integer type data is 16-bit integer value data.
Word devices are used in increments of 1 point.
Data ranges are shown below.
Decimal representation Hexadecimal representation
Data range K-32768 to K32767 H0000 to HFFFF
(b) 32-bit integer type data
The 32-bit integer type data is 32-bit integer value data.
Word devices are used in increments of 2 points: (specified device No.),
(specified device No.+1). Data ranges are shown below.
Decimal representation Hexadecimal representation
Data range K-2147483648L to K2147483647L H00000000L to HFFFFFFFFL
(c) 64-bit floating-point type data
The 64-bit floating-point type data is IEEE-formatted, 64-bit floating-point
value data.
Word devices are used in increments of 4 points: (specified device No.),
(specified device No.+1), (specified device No.+2), (specified device
No.+3).
1) The internal bit locations are shown below.
b63 b62 b52
b51
b0
b51 to b0 (52 bits)
Decimal field
b62 to b52 (11 bits )
Bias exponent field
b63 (1 bit)
Sign bit field
(Specified device number+0) (+1) (+2) (+3)
2) The represented value is shown below. (The bias value is H3FF.)
(-1)
[Sign bit field]
(1.0+[decimal field]) 2
([Bias exponent field]-[bias value])