Chapter 6. Performance Considerations 415
1st ed., 6/30/04 - 312579601
If ejects and/or enters of large numbers of cartridges are frequent, you may want to set
higher CAP preferences for enhanced CAPs.
Refer to the HSC Operator’s Guide for information about the CAPPref command.
Use SMF Records to Collect Performance Data
Library performance data can be accumulated from SMF records. The SMF operand of the
SLILIBRY macro for LIBGEN or the SMF parameter of the HSC SET utility determines
the SMF record type written by the HSC. The SCP SET PERFLOG command is used to
enable or disable recording of SMF data and to close the data file (and reopen if enabled).
The command also allows specifying which SMF record subtypes are to be collected.
Refer to the HSC Operator’s Guide for additional details.
With SMF recording enabled, a record of various library activities is made for the
specified record subtypes. Each library activity, such as each time the VIew command
(optional subtype(8)) is used, each time a cartridge is entered or ejected, etc., is recorded
as an SMF subtype record.
The performance log data file that is created can be used to analyze library performance.
Software analytical tools can be used to manipulate the data and create various
performance statistics.
Refer to Appendix C, “Record Formats” on page 497 for detailed information about SMF
record subtypes. Refer to “SET Utility” on page 299 for information about the SET utility,
syntax, and parameters.
Use PARMLIB to Define Static Parameters
PARMLIB control statements can be specified to the HSC startup SLKJCL file. At HSC
installation, the various performance criteria specified by the control statements are
statically established. The systems programmer may specify these control statements to be
executed when the HSC software is initialized. Most of the statically set parameters can be
changed at any time after initialization by issuing an appropriate operator command.
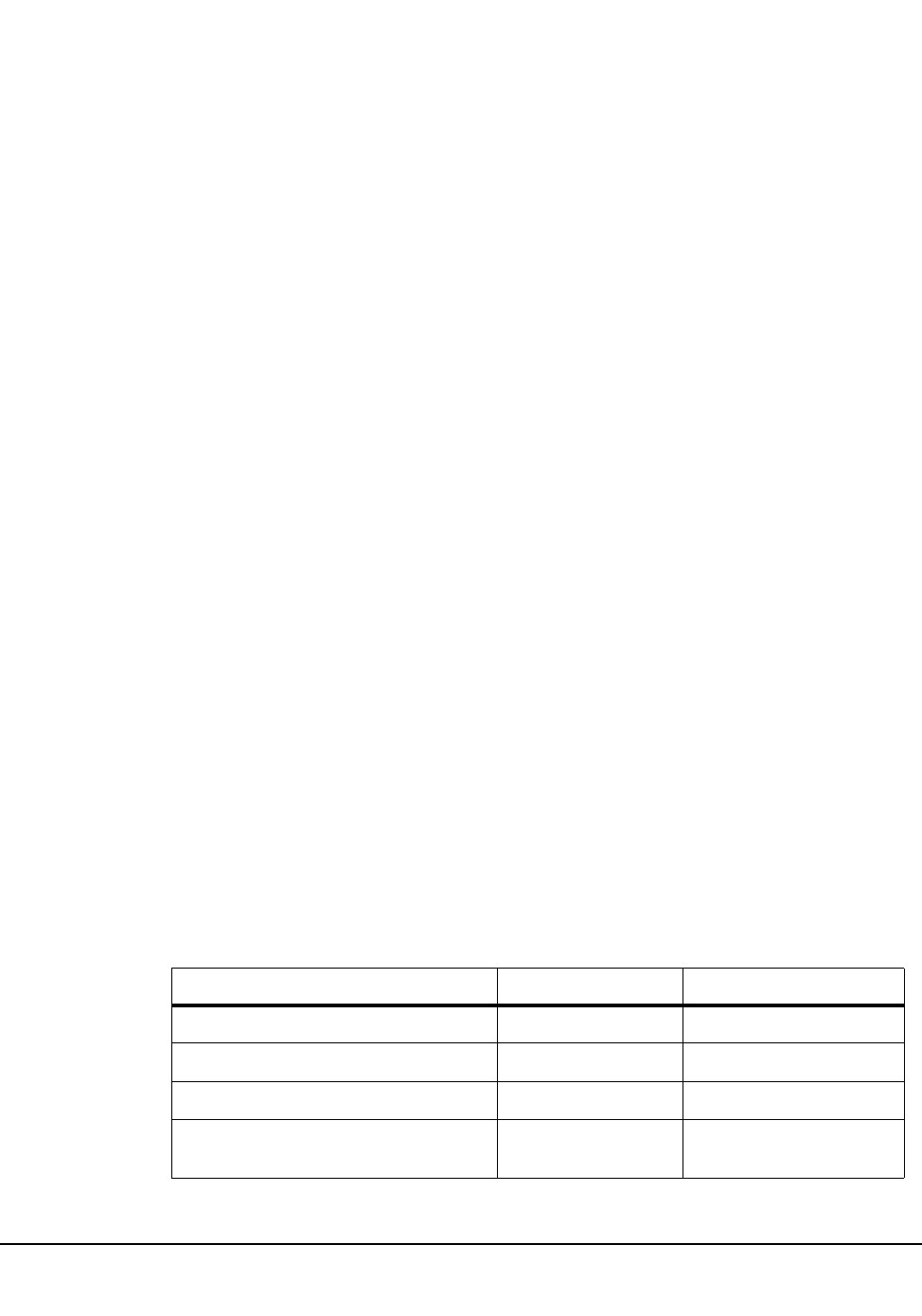
Table 28 summarizes the PARMLIB control statements with corresponding operator
commands. Any of the PARMLIB control statements can be used to improve various
performance aspects of library operation.
Table 28. Performance Parameters Controlled by PARMLIB Control Statements
Performance Parameter Control Statement Operator Command
CAP Preference CAPPref CAPPref
Control Data Set Definition CDSDEF
Host-to-Host Communications Path COMMPath COMMPath
Control Message Prefix, Eid, Fid, and
Hostid
EXECPARM


















