CHP. 9 EDITING, REPAIRING, AND SYNTHESIZING AUDIO
139
Interpolating new audio
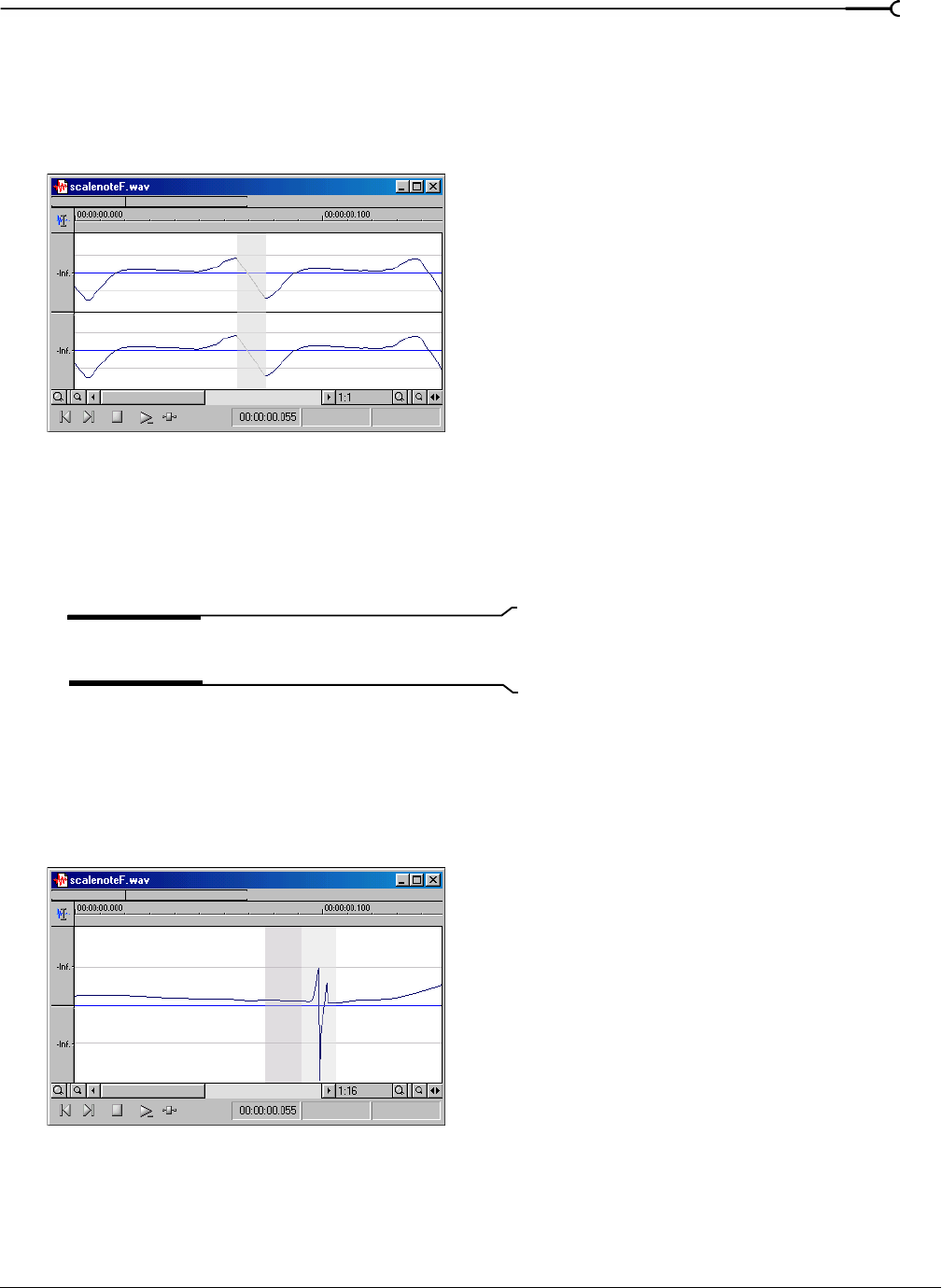
This is the most basic method of repairing glitches. Sound Forge simply interpolates new audio data based on
the data at the beginning and end of the selection. This method results in a straight line connecting the
beginning and end of the selection. Interpolation should only be used to repair small (less than 2 ms)
glitches.
1.
Open the file containing the glitch.
2.
Right-click the data window and choose Zoom from the shortcut menu, and choose In Full from the
submenu. If you are using the full version of Sound Forge, the file displays at a 24:1 zoom ratio. If you are
using Screenblast Sound Forge, the file displays at a 1:1 zoom ratio.
3.
Create a selection containing the glitch.
Tip:
To improve the accuracy of this feature, the selection
should be as small as possible while still containing the glitch.
4.
From the Tools menu, choose Repair, and choose Interpolate from the submenu. Sound Forge replaces the
glitch data with interpolated data.
Replacing audio with preceding data
The Replace tool allows you to repair audio files by replacing the damaged data with the data immediately
preceding it. This repair method is useful for repairing longer glitches such as needle drops and scratches.
1.
Open the file containing the glitch.
Data is interpolated within the selection
Interpolated data
Selection is replaced with data preceding it
Selection data
Replacement data
