13 - 2
Chapter 13 Control Sub Functions
13.1 Outline of sub functions
"Sub functions" are functions that compensate, limit, add functions, etc., to the control
when the main functions are executed. These sub functions are executed by
parameter settings, operation from GX Works2, sub function sequence programs, etc.
13.1.1 Outline of sub functions
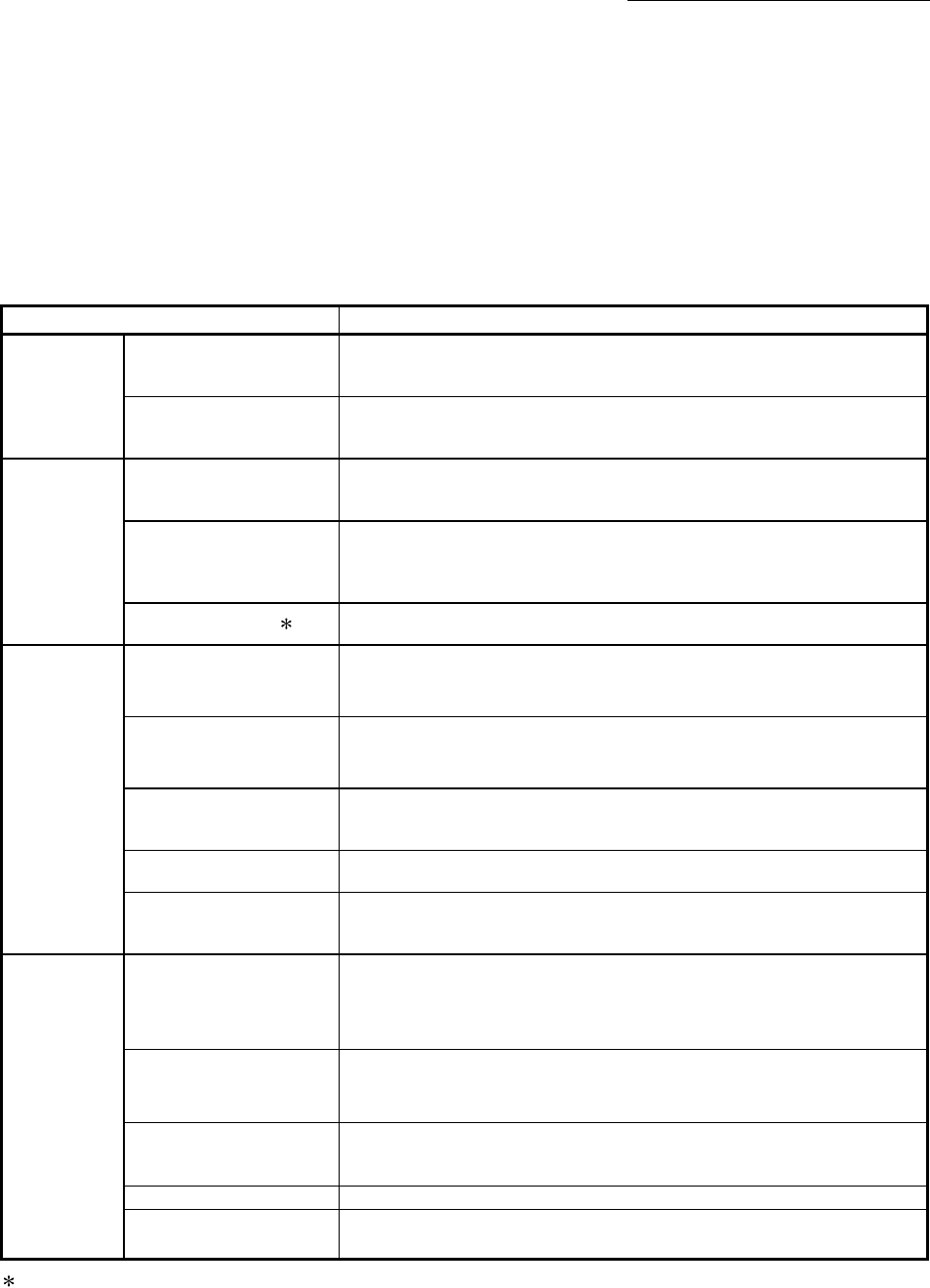
The following table shows the types of sub functions available.
Sub function Details
Functions
characteristic
to machine
OPR
OPR retry function
This function retries the OPR with the upper/lower limit switches during
machine OPR. This allows machine OPR to be carried out even if the axis is
not returned to before the near-point dog with JOG operation, etc.
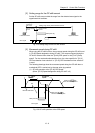
OP shift function
After returning to the machine OP, this function offsets the position by the
designated distance from the machine OP position and sets that position as
the OP address.
Functions that
compensate
control
Backlash compensation
function
This function compensates the mechanical backlash. Feed command
equivalent to the set backlash amount are output each time the movement
direction changes.
Electronic gear function
By setting the movement amount per pulse, this function can freely change
the machine movement amount per commanded pulse.
When the movement amount per pulse is set, a flexible positioning system
that matches the machine system can be structured.
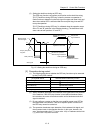
Near pass function 1
This function suppresses the machine vibration when the positioning data is
switched during continuous path control in the interpolation control.
Functions that
limit control
Speed limit function
If the command speed exceeds "[Pr.8] Speed limit value" during control, this
function limits the commanded speed to within the "[Pr.8] Speed limit value"
setting range.
Torque limit function
If the torque generated by the servomotor exceeds "[Pr.17] Torque limit
setting value" during control, this function limits the generated torque to
within the "[Pr.17] Torque limit setting value" setting range.
Software stroke limit
function
If a command outside of the upper/lower limit stroke limit setting range, set in
the parameters, is issued, this function will not execute positioning for that
command.
Hardware stroke limit
function
This function carries out deceleration stop with the hardware stroke limit
switch.
Forced stop function
This function is stopped the all axes of the servo amplifier when the forced
stop input signal of the Simple Motion module external input connection
connector is turned ON.
Functions that
change control
details
Speed change function
This function changes the speed during positioning.
Set the changed speed in the speed change buffer memory ([Cd.14] New
speed value), and change the speed with the speed change request ([Cd.15]
Speed change request).
Override function
This function changes the speed within a percentage of 1 to 300% during
positioning. This is executed using "[Cd.13] Positioning operation speed
override".
Acceleration/deceleration
time change function
This function changes the acceleration/deceleration time during speed
change. (Functions added to the speed change function and override
function.)
Torque change function This function changes the "torque limit value" during control.
Target position change
function
This function changes the target position during the execution of positioning.
At the same time, this also can change the speed.
1: The near pass function is validated only when the machine of the standard specification carries out the position control
with the continuous path control mode. It cannot be invalidated with parameters.