Security Services > RBL Filter
754
SonicOS Enhanced 4.0 Administrator Guide
Note Most spam today is known to be sent from hijacked or zombie machines running a thin
SMTP server implementation, unbeknownst to the hosts operator. These zombie machines
rarely attempt to retry failed delivery attempts, as would be the behavior of a legitimate
SMTP server. As such, once the delivery attempt is thwarted by the SonicWALL RBL filter,
no subsequent delivery attempts for that same piece of spam will be made.
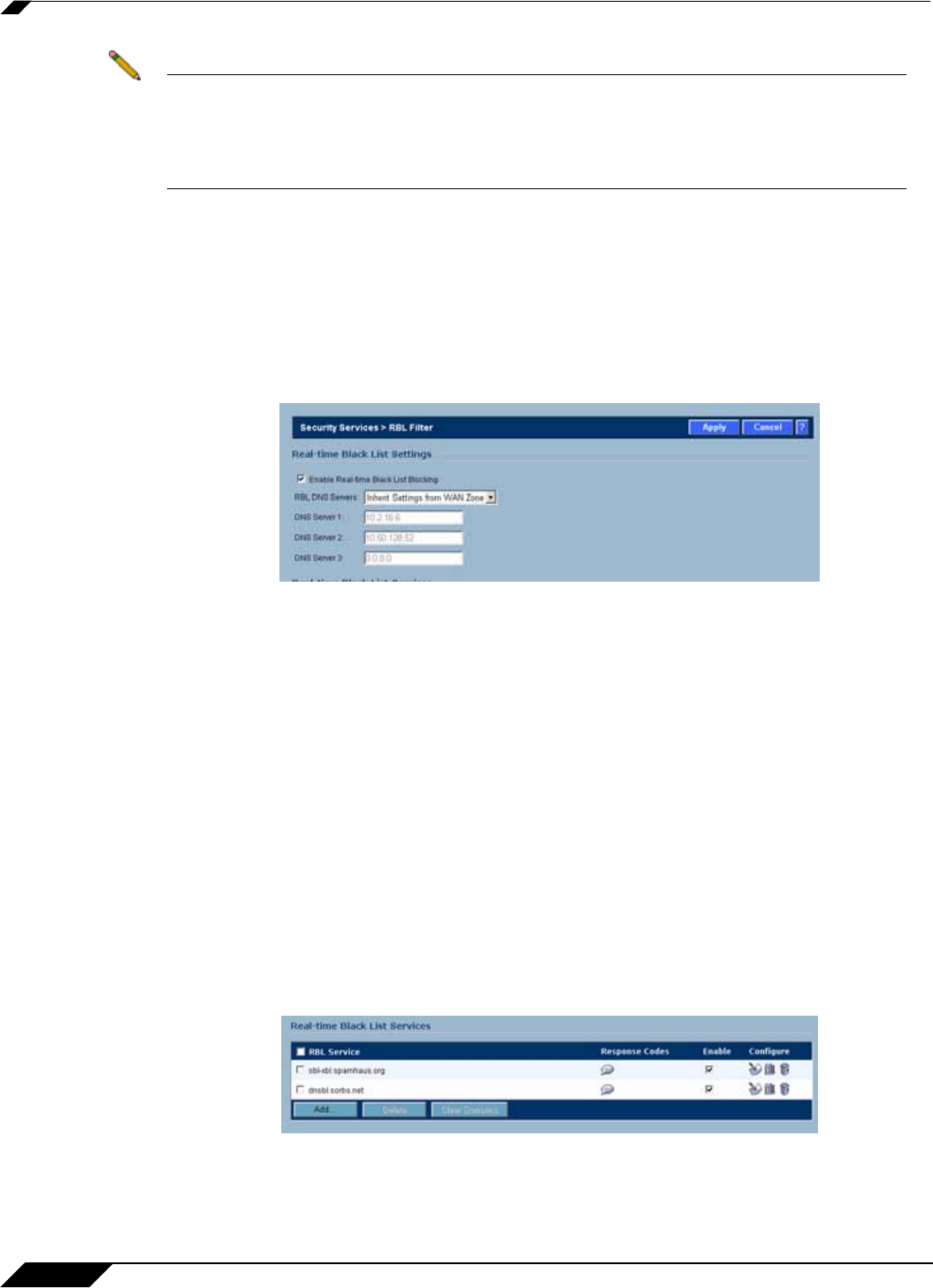
Security Services > RBL Filter
When Enable Real-time Black List Blocking in enabled on the Security Services > RBL
Filter page, inbound connections from hosts on the WAN, or outbound connections to hosts on
the WAN are checked against each enabled RBL service with a DNS request to the DNS
servers configured under RBL DNS Servers.
The RBL DNS Servers menu allows you to specify the DNS servers. You can choose Inherit
Settings from WAN Zone or Specify DNS Servers Manually. If you select Specify DNS
Servers Manually, enter the DNS server addresses in the DNS Server fields.
The DNS responses are collected and cached. If any of the queries result in a blacklisted
response, the server will be filtered. Responses are cached using TTL values, and non-
blacklisted responses are assigned a cache TTL of 2 hours. If the cache fills up, then cache
entries are discarded in a FIFO (first-in-first-out) fashion.
The IP address check uses the cache to determine if a connection should be dropped. Initially,
IP addresses are not in the cache and a DNS request must be made. In this case the IP address
is assumed innocent until proven guilty, and the check results in the allowing of the connection.
A DNS request is made and results are cached in a separate task. When subsequent packets
from this IP address are checked, if the IP address is blacklisted, the connection will be
dropped.
Adding RBL Services
You can add additional RBL services the Real-time Black List Services section.


















