Network > Routing
237
SonicOS Enhanced 4.0 Administrator Guide
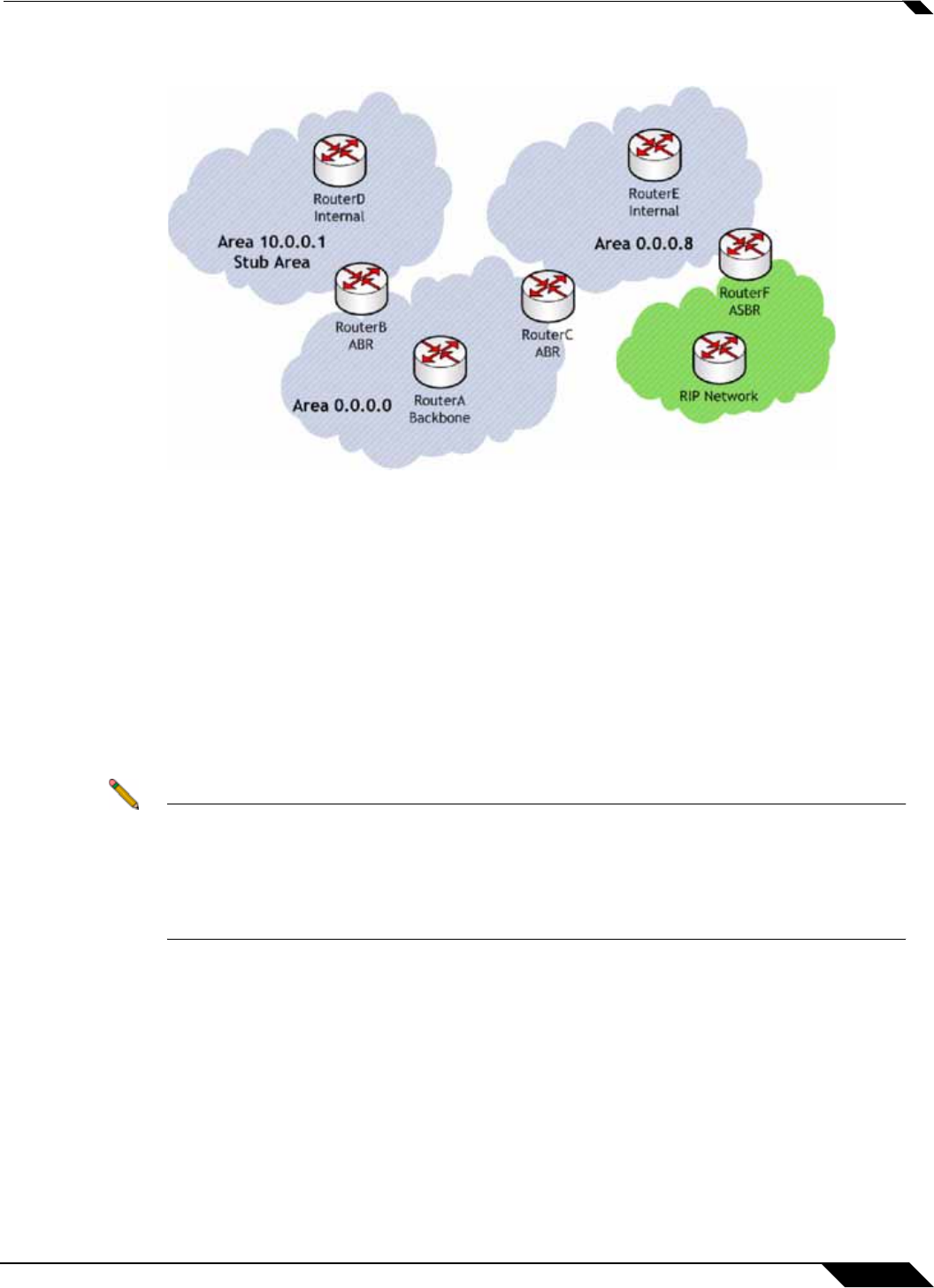
• Router Types – OSPF recognizes 4 types of routers, based on their roles:
• IR (Internal Router) - A router whose interfaces are all contained within the same area. An
internal router’s LSDB only contains information about its own area.
• ABR (Area Border Router) – A router with interfaces in multiple areas. An ABR maintains
LSDB’s for each area to which it is connected, one of which is typically the backbone.
• Backbone Router – A router with an interface connected to area 0, the backbone.
• ASBR (Autonomous System Boundary Router) – A router with an interface connected to a
non-OSPF AS (such as a RIP network) which advertises external routing information from
that AS into the OSPF AS.
Configuring Advanced Routing Services
Note ARS is a fully featured multi-protocol routing suite. The sheer number of configurable
options and parameters provided is incongruous with the simplicity of a graphical user
interface. Rather than limiting the functionality of ARS, an abbreviated representation of its
capabilities has been rendered in the GUI, providing control over the most germane routing
features, while the full command suite is available via the CLI. The ARS CLI can be
accessed from an authenticated CLI session, and contains 3 modules:
• route ars-nsm – The Advanced Routing Services Network Services Module. This
component provides control over core router functionality, such as interface bindings and
redistributable routes.
• route ars-rip – The RIP module. Provides control over the RIP router.
• route ars-ospf – The OSPF module. Provides control over the OSPF router.
In general, all of the functionality needed to integrate the SonicWALL into most RIP and
OSPF environments is available through the web-based GUI. The additional capabilities of
the CLI will make more advanced configurations possible. Please refer to the appendix for
the full set of ARS CLI commands.


















