Network > NAT Policies
252
SonicOS Enhanced 4.0 Administrator Guide
• Round Robin – Source IP cycles through each live load-balanced resource for each
connection. This method is best for equal load distribution when persistence is not required.
• Block Remap/Symmetrical Remap – These two methods are useful when you know the
source IP addresses/networks (e.g. when you want to precisely control how traffic from one
subnet is translated to another).
• Random Distribution – Source IP connects to Destination IP randomly. This method is
useful when you wish to randomly spread traffic across internal resources.
• NAT Method – This drop-down allows the user to specify one of five load balancing
methods: Sticky IP, Round Robin, Block Remap, Symmetric Remap, or Random
Distribution. For most purposes, Sticky IP is preferred.
• Enable Probing – When checked, the SonicWALL will use one of two methods to probe
the addresses in the load-balancing group, using either a simple ICMP ping query to
determine if the resource is alive, or a TCP socket open query to determine if the resource
is alive. Per the configurable intervals, the SonicWALL can direct traffic away from a non-
responding resource, and return traffic to the resource once it has begun to respond again.
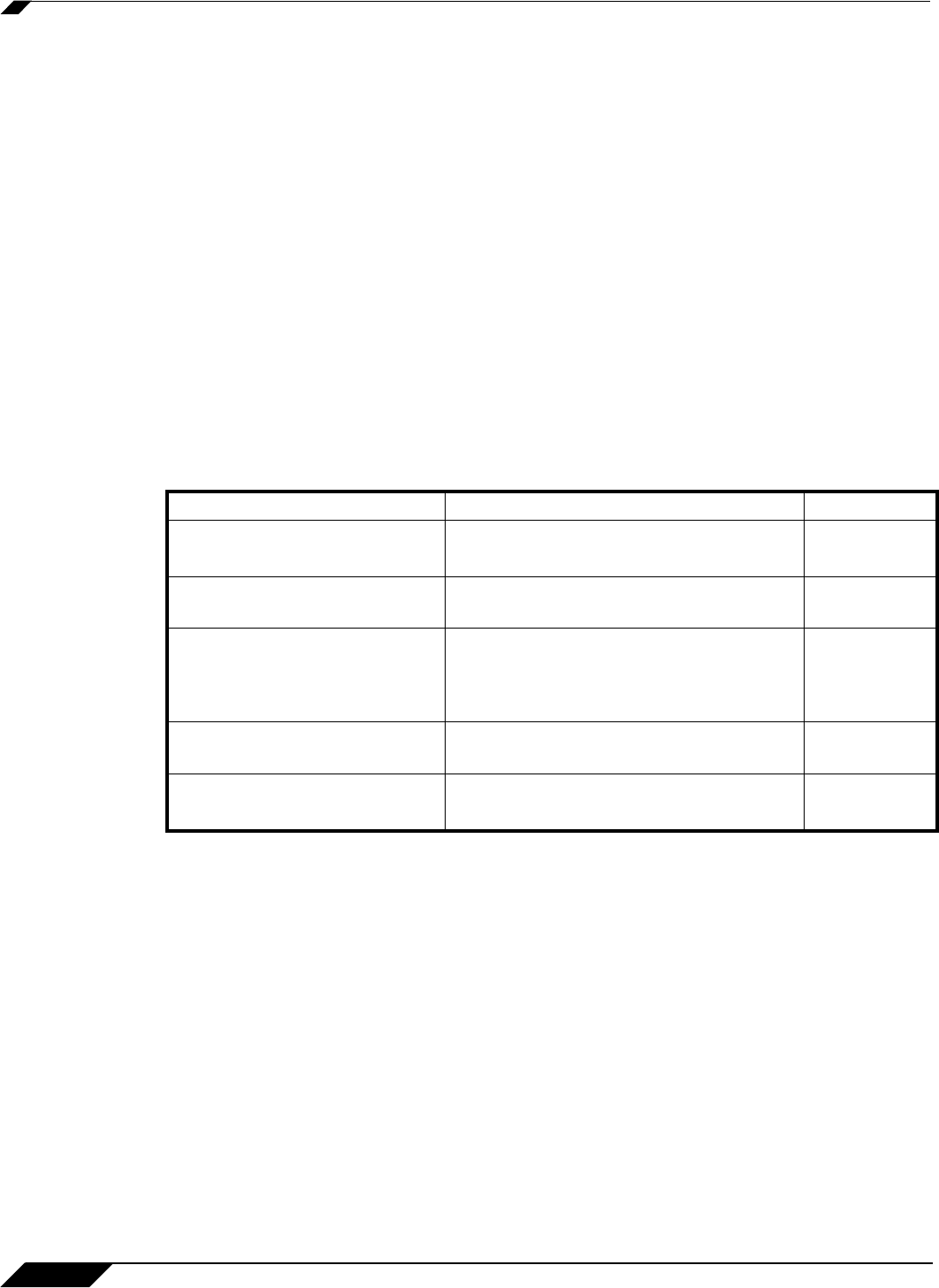
Which NAT LB Method Should I Use?
Caveats
• The NAT Load Balancing Feature is only available in SonicOS Enhanced 4.0 and newer.
• Only two health-check mechanisms at present (ICMP ping and TCP socket open).
• No higher-layer persistence mechanisms at present (Sticky IP only).
• No “sorry-server” mechanism at present if all servers in group are not responding.
• No “round robin with persistence” mechanism at present.
• No “weighted round robin” mechanism at present.
• No method for detecting if resource is strained, at present.
• While there is no limit to the number of internal resources the SonicWALL appliance can
load-balance to, and there no limit to the number of hosts it can monitor, abnormally large
load-balancing groups (25+resources) may impact performance.
Requirement Deployment Example NAT LB Method
Distribute load on server equally
without need for persistence
External/ Internal servers (i.e. Web, FTP,
etc.)
Round Robin
Indiscriminate load balancing
without need for persistence
External/ Internal servers (i.e. Web, FTP,
etc.)
Random
Distribution
Requires persistence of client
connection
E-commerce site, Email Security, SSL-VPN
appliance
(Any publicly accessible servers requiring
persistence)
Sticky IP
Precise control of remap of source
network to a destination range
LAN to DMZ Servers
E-mail Security, SSL-VPN
Block Remap
Precise control of remap of source
network and destination network
Internal Servers (i.e. Intranets or Extranets) Symmetrical
Remap


















