Network > Routing
230
SonicOS Enhanced 4.0 Administrator Guide
To test the Telnet policy-based route, telnet to route-server.exodus.net and when logged in,
issue the who command. It displays the IP address (or resolved FQDN) of the WAN IP address
of the secondary WAN interface and not the primary WAN interface.
Advanced Routing Services (OSPF and RIP)
In addition to Policy Based Routing and RIP advertising, SonicOS Enhanced offers the option
of enabling Advanced Routing Services (ARS). Advanced Routing Services provides full
advertising and listening support for the Routing Information Protocol (RIPv1 - RFC1058) and
(RIPv2 - RFC2453), and Open Shortest Path First (OSPFv2 – RFC2328). Advanced Routing
Service should only be enabled by those environments requiring support for either or both of
these dynamic routing protocols.
RIP and OSPF are Interior Gateway Protocols (IGP) that are both widely used by networks of
various sizes to automate the process of route distribution. RIP is commonly used within
smaller networks, while OSPF is used by larger networks, although network size should not be
the only factor used to determine the appropriateness of one protocol over the other – network
speed, interoperability requirements, and relative overall complexity, for example, should also
be considered. RIPv1 and RIPv2 are both supported by ARS, the largest differences between
the two being that RIPv2 supports VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masks), authentication, and
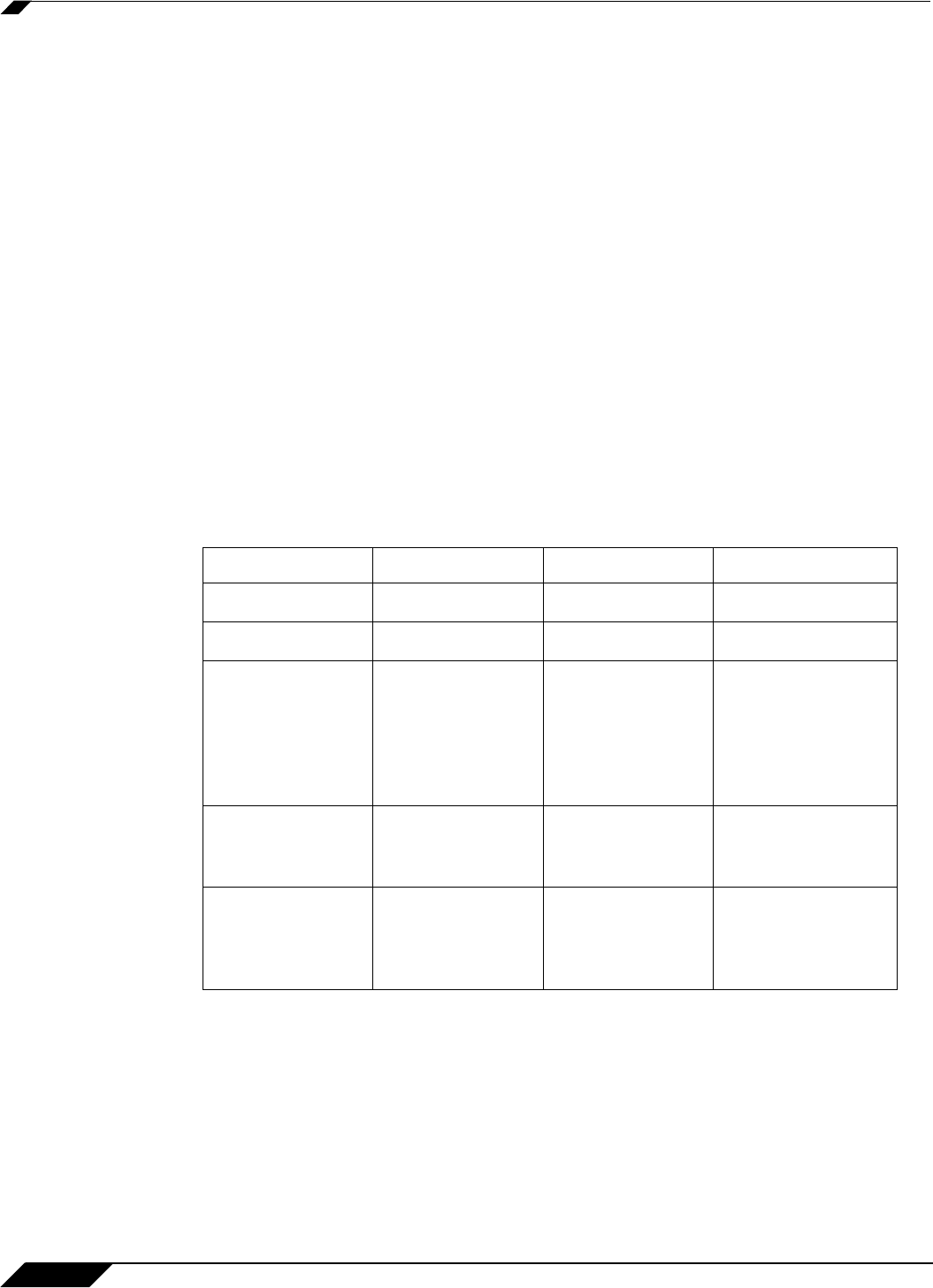
routing updates. The following table illustrates the major differences between RIPv1, RIPv2,
and OSPFv2:
RIPv1 RIPv2 OSPFv2
Protocol metrics Distance Vector Distance Vector Link State
Maximum Hops 15 15 Unlimited
Routing table
updates
Full table
broadcast
periodically,
slower
convergence
Full table
broadcast or
multicast
periodically,
slower
convergence
Link state
advertisement
multicasts,
triggered by
changes, fast
convergence
Subnet Sizes
Supported
Only class-based
(a/b/c) subnets
support
Class-based only VLSM
Autonomous
system topology
Indivisible and flat Indivisible and flat Area based,
allowing for
segmentation and
aggregation


















