NOTE: Alternatively, you can reset the interface by shutting it down using the shutdown command
and then re-enabling it using the no shutdown command.
• Reset interfaces in the ERR_Disabled state caused by a learning limit violation or station move
violation.
EXEC Privilege mode
mac learning-limit reset
• Reset interfaces in the ERR_Disabled state caused by a learning limit violation.
EXEC Privilege mode
mac learning-limit reset learn-limit-violation [interface | all]
• Reset interfaces in the ERR_Disabled state caused by a station move violation.
EXEC Privilege mode
mac learning-limit reset station-move-violation [interface | all]
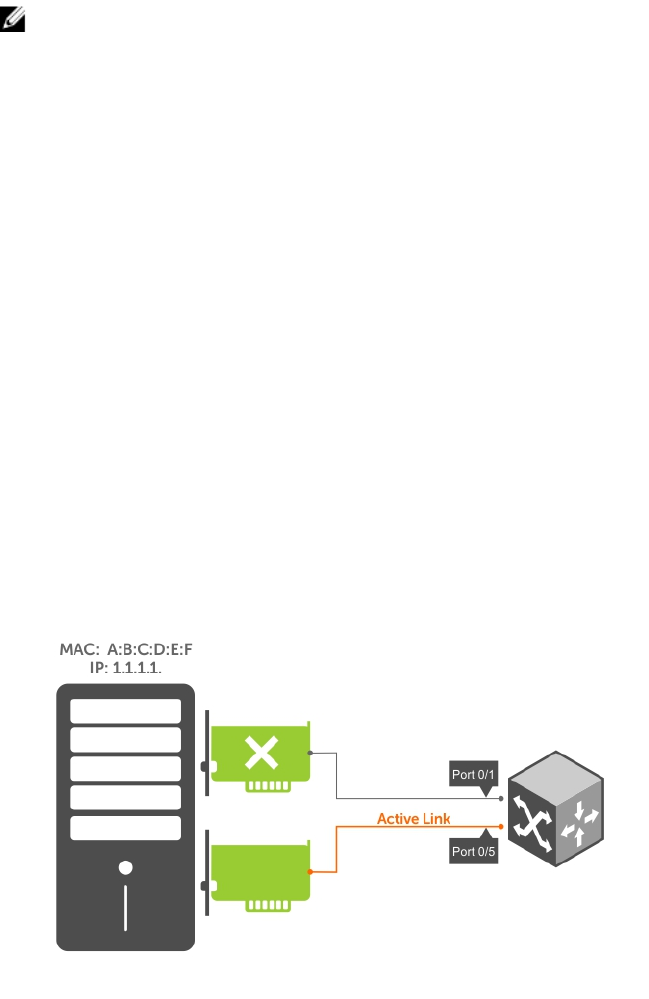
NIC Teaming
Network interface controller (NIC) teaming is a feature that allows multiple network interface cards in a
server to be represented by one MAC address and one IP address in order to provide transparent
redundancy, balancing, and to fully utilize network adapter resources.
The following illustration shows a topology where two NICs have been teamed together. In this case, if
the primary NIC fails, traffic switches to the secondary NIC because they are represented by the same set
of addresses.
Figure 64. Redundant NICs with NIC Teaming
When you use NIC teaming, consider that the server MAC address is originally learned on Port 0/1 of the
switch (shown in the following) and Port 0/5 is the failover port. When the NIC fails, the system
automatically sends an ARP request for the gateway or host NIC to resolve the ARP and refresh the egress
interface. When the ARP is resolved, the same MAC address is learned on the same port where the ARP is
resolved (in the previous example, this location is Port 0/5 of the switch). To ensure that the MAC address
is disassociated with one port and re-associated with another port in the ARP table, configure the mac-
534
Layer 2


















