• You can configure shared LAG state tracking on one side of a link or on both sides.
• If a LAG that is part of a failover group is deleted, the failover group is deleted.
• If a LAG moves to the Down state due to this feature, its members may still be in the Up state.
LACP Basic Configuration Example
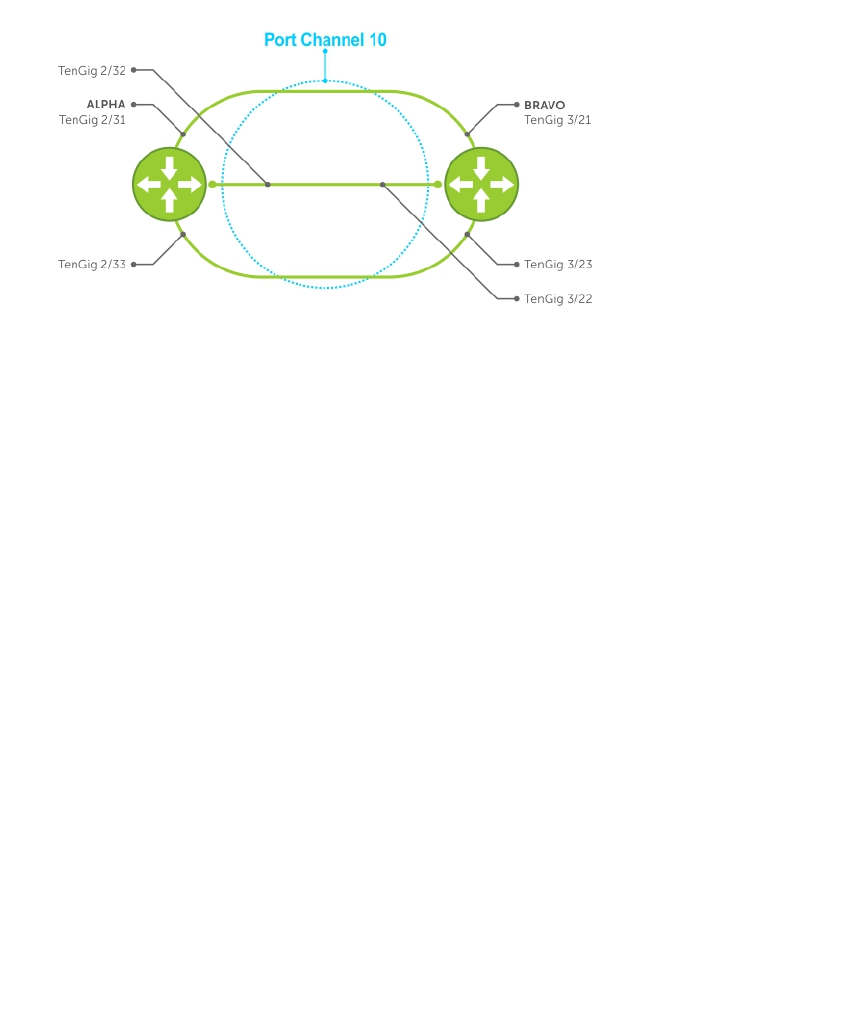
The screenshots in this section are based on the following example topology. Two routers are named
ALPHA and BRAVO, and their hostname prompts reflect those names.
Figure 57. LACP Basic Configuration Example
Configure a LAG on ALPHA
The following example creates a LAG on ALPHA.
Example of Configuring a LAG
Alpha(conf)#interface port-channel 10
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#no ip address
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#switchport
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#no shutdown
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#show config
!
interface Port-channel 10
no ip address
switchport
no shutdown
!
Alpha(conf-if-po-10)#
Example of Viewing a LAG Port Configuration
The following example inspects a LAG port configuration on ALPHA.
Alpha#show int tengig 2/31
TengigabitEthernet 2/31 is up, line protocol is up
Port is part of Port-channel 10
Hardware is Dell Force10Eth, address is 00:01:e8:06:95:c0
Current address is 00:01:e8:06:95:c0
Interface Index is 109101113
Port will not be disabled on partial SFM failure
Internet address is not set
MTU 1554 bytes, IP MTU 1500 bytes
LineSpeed 1000 Mbit, Mode full duplex, Slave
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
521


















