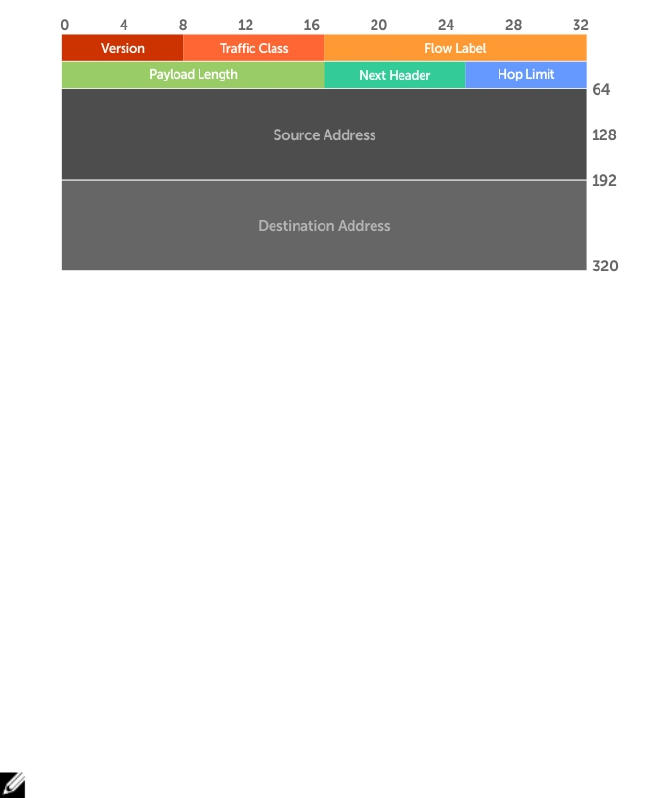
IPv6 Header Fields
The 40 bytes of the IPv6 header are ordered, as shown in the following illustration.
Figure 49. IPv6 Header Fields
Version (4 bits)
The Version field always contains the number 6, referring to the packet’s IP version.
Traffic Class (8 bits)
The Traffic Class field deals with any data that needs special handling. These bits define the packet
priority and are defined by the packet Source. Sending and forwarding routers use this field to identify
different IPv6 classes and priorities. Routers understand the priority settings and handle them
appropriately during conditions of congestion.
Flow Label (20 bits)
The Flow Label field identifies packets requiring special treatment in order to manage real-time data
traffic.
The sending router can label sequences of IPv6 packets so that forwarding routers can process packets
within the same flow without needing to reprocess each packet’s header separately.
NOTE: All packets in the flow must have the same source and destination addresses.
Payload Length (16 bits)
The Payload Length field specifies the packet payload. This is the length of the data following the IPv6
header. IPv6 Payload Length only includes the data following the header, not the header itself.
The Payload Length limit of 2 bytes requires that the maximum packet payload be 64 KB. However, the
Jumbogram option type Extension header supports larger packet sizes when required.
Next Header (8 bits)
The Next Header field identifies the next header’s type. If an Extension header is used, this field contains
the type of Extension header (as shown in the following table). If the next header is a transmission control
protocol (TCP) or user datagram protocol (UDP) header, the value in this field is the same as for IPv4. The
Extension header is located between the IP header and the TCP or UDP header.
IPv6 Routing
461


















