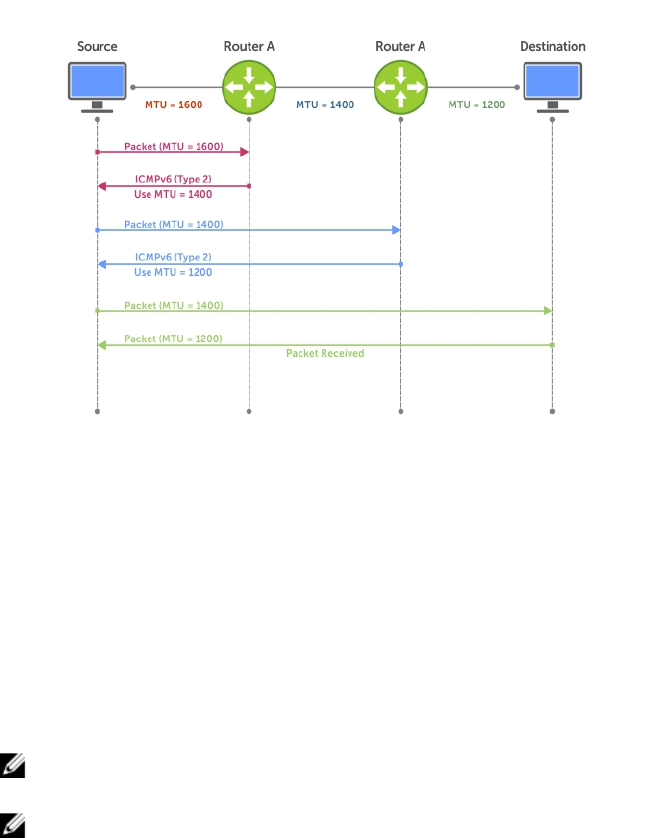
Figure 50. Path MTU Discovery Process
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery
The IPv6 neighbor discovery protocol (NDP) is a top-level protocol for neighbor discovery on an IPv6
network.
In place of address resolution protocol (ARP), NDP uses “Neighbor Solicitation” and “Neighbor
Advertisement” ICMPv6 messages for determining relationships between neighboring nodes. Using these
messages, an IPv6 device learns the link-layer addresses for neighbors known to reside on attached links,
quickly purging cached values that become invalid.
NOTE: If a neighboring node does not have an IPv6 address assigned, it must be manually pinged to
allow the IPv6 device to determine the relationship of the neighboring node.
NOTE: To avoid problems with network discovery, Dell Networking recommends configuring the
static route last or assigning an IPv6 address to the interface and assigning an address to the peer
(the forwarding router’s address) less than 10 seconds apart.
With ARP, each node broadcasts ARP requests on the entire link. This approach causes unnecessary
processing by uninterested nodes. With NDP, each node sends a request only to the intended destination
via a multicast address with the unicast address used as the last 24 bits. Other hosts on the link do not
participate in the process, greatly increasing network bandwidth efficiency.
468
IPv6 Routing


















