61
Operational Overview
regardless of the starting point. A Rotary Plus Index moves to the specified position, but is forced in a positive direction.
Similarly, a Rotary Minus Index moves to the specific position, but is forced in a negative direction.
Rotary Plus and Minus Indexes are usually used in rotary applications, therefore the rotary rollover feature on the User Units
view in PowerTools Pro software must be enabled to use them.
1. In the following examples the term “D” = (absolute position specified) - (current position). If “D” is negative, motion in
the negative direction is implied.
2. In the following examples the Rotary Rollover parameter on the Setup - Position view is set to 360.00°. This means that
with each revolution of the motor (or rotary table), feedback will count up to 359.99°, then roll over to Ø°.
Indexes with Rotary Rollover Enabled
Incremental move distances can be outside of the rotary rollover range. See “Setting Up Parameters” on page 3 section for
an explanation of Rotary Rollover.
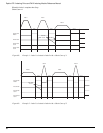
Example 1: If the starting position is at Ø° and 720° is the specified distance, an Incremental index would move 2 revolutions
in the positive direction. At the completion of this index the motor position would be Ø°.
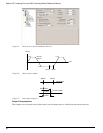
Absolute indexes will take the shortest path to the specified position. Absolute index positions must be within the rotary
rollover range.
Example 2: If the starting position is at 90° and 80° is the specified position, an Absolute index would travel 10° in the
negative direction. At the completion of this index the motor position would be 80°.
Example 3: If the starting position is 45° and 315° is the specified position, an Absolute index would travel 90° in the
negative direction because that is the shortest path between 45° and 315°.
Rotary Plus indexes will move to the specified position and are forced in a positive (or plus) direction. Rotary Plus index
distances must be within the rotary rollover range.
Example 4: As in example 2 above, the starting position is at 90° and 80° is the specified position. A Rotary Plus index would
travel 350° in the positive direction. At the completion of this index the motor position would be 80°.
Example 5: If the starting position is 10° and the specified position is 350°, a Rotary Plus index will travel 340° in the positive
direction.
Rotary Minus indexes move to the specified position, but are forced to travel in the negative (or minus) direction. Rotary
Minus index positions must be within the rotary rollover range.
Example 6: As in examples 2 and 4 above, the starting position is at 90° and 80° is the specified position. A Rotary Minus
index would travel 10° in the negative direction. At the completion of this index the motor position would be 80°.
Example 7: If the starting position is 15° and the specified position is 270°, a Rotary Minus index would travel 105° in the
negative direction.
Index Parameters
Distance/Position
The Distance/Position parameter specifies the distance the index will travel (incremental index), the absolute position the
index will move to (absolute index), or the limit distance (registration indexes).
Velocity
The Velocity parameter specifies the peak velocity used for the index. The velocity parameter is unsigned and must be greater
than zero.
Acceleration
The Acceleration parameter specifies the acceleration value to be used during the index.
Deceleration
The Deceleration parameter specifies the deceleration value to be used during the index.