106
Epsilon EP-I Indexing Drive and FM-2 Indexing Module Reference Manual
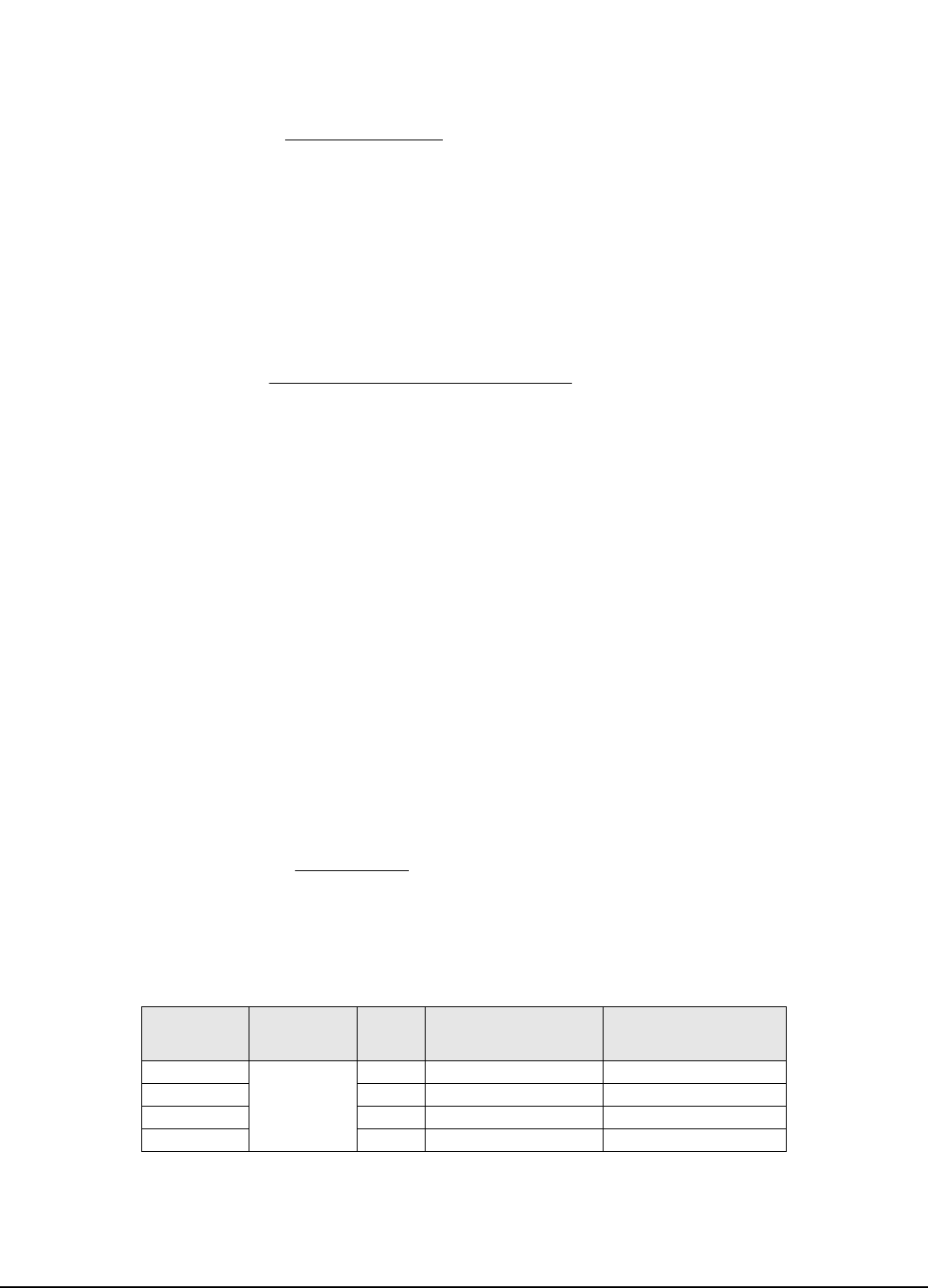
3. Use the appropriate formula below to calculate the inertia.
For horizontal loads or counterbalanced vertical loads use the following formula:
Where:
IR = Inertia Ratio
R = ramp in ms/kRPM
Ta = (unsigned) percent continuous torque required during acceleration ramping (0 - 300)
Td = (unsigned) percent continuous torque required during deceleration ramping (0 - 300)
Vm = motor constant value from Table 18 below
For un-counter balanced vertical loads use the following formula:
Where:
IR = Inertia Ratio
R = ramp in ms/kRPM
Vm = motor constant value from the table below
Tau = (unsigned) percent continuous torque required during acceleration ramping while moving up (against the
constant force)
Tdu = (unsigned) percent continuous torque required during deceleration ramping while moving up (against the
constant force)
Tad = (unsigned) percent continuous torque required during acceleration ramping while moving down (aided by the
constant force)
Tdd = (unsigned) percent continuous torque required during deceleration ramping while moving down (aided by the
constant force)
Ramp Units Conversion
If you are using an external position controller to generate motion you may need to connect the ramp units as desired below.
Many position controllers define acceleration in units per sec
2
. The formulas above use ms/kRPM. Make sure you make this
conversion when entering the information into the formula.
Conversion Formula:
Where:
MPK = accel ramp in ms/kRPM
RPSS = accel ramp in revolutions per second
2
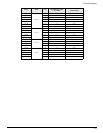
Motor Drive Vm
Percent Continuous/volt
(default scaled Torque
Command)
RPM /volt (default scaled
Actual Velocity)
MG-205
EN-204
4.77 30 600
MG-208 5.11 30 600
MG-316 3.17 30 600
NT-320 4.3 30 600
1
2000
Td)) Vm (Ta (R
IR −
+
•
=
1
4000
Tdd)) Tad Tud (Tau Vm (R
IR −
+
+
+
•
=
60) (RPSS
10
MPK
6
•
=