Theory of Operation Teledyne API – Model T300/T300M CO Analyzer
302
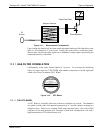
INTERFERENCE AND SIGNAL TO NOISE REJECTION
If an interfering gas, such as H
2
O vapor is introduced into the sample chamber, the
spectrum of the IR beam is changed in a way that is identical for both the reference and
the measurement cells, but without changing the ratio between the peak heights of CO
MEAS and CO REF. In effect, the difference between the peak heights remains the
same.
IR shining through both cells is
affected equally by interfering
gas in the Sample Chamber
M/R
is Shifted
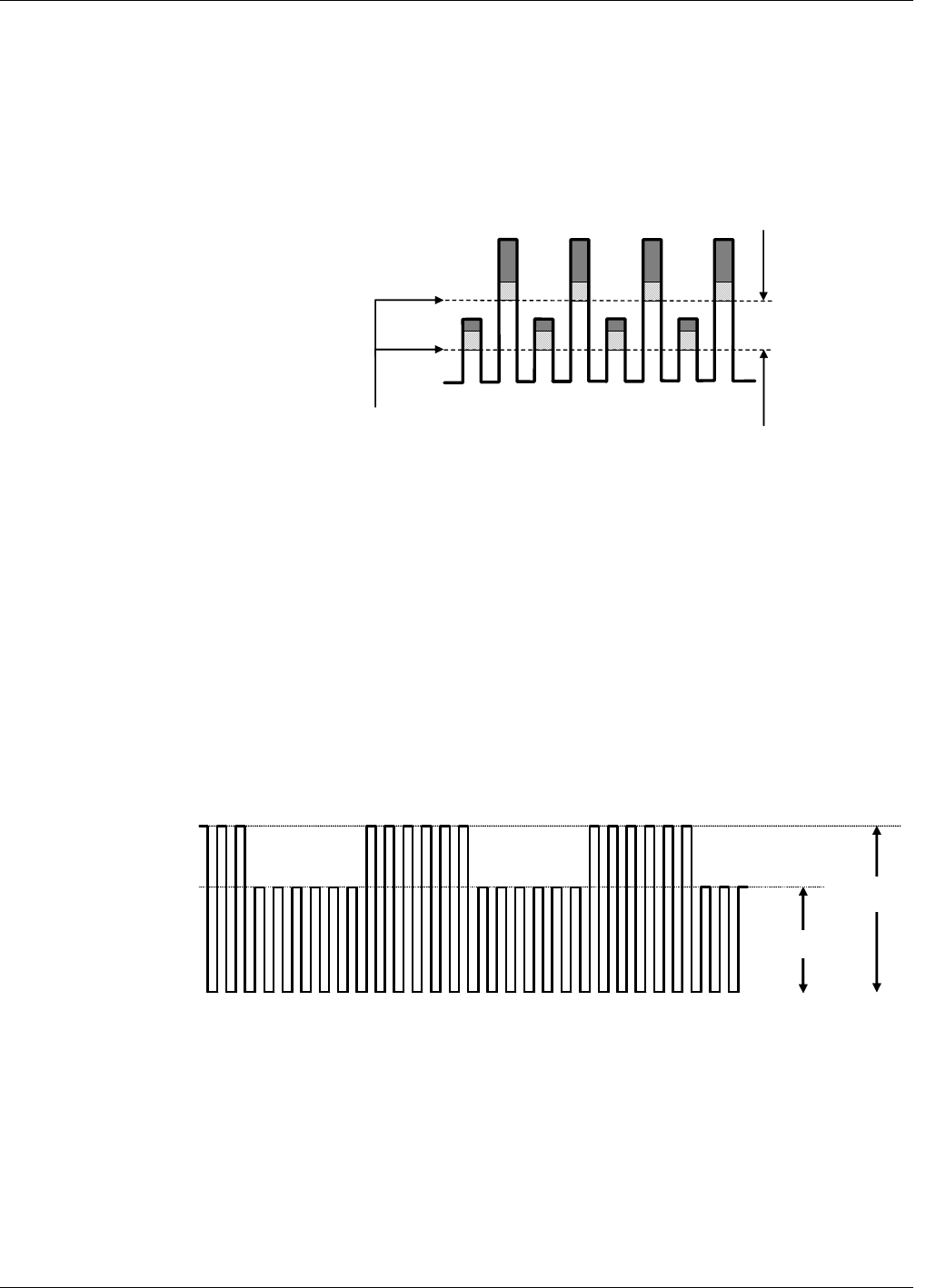
Figure 13-5: Effects of Interfering Gas on CO MEAS & CO REF
Thus, the difference in the peak heights and the resulting M/R ratio is only due to CO
and not to interfering gases. In this case, GFC rejects the effects of interfering gases and
so that the analyzer responds only to the presence of CO.
To improve the signal-to-noise performance of the IR photo-detector, the GFC Wheel
also incorporates an optical mask that chops the IR beam into alternating pulses of light
and dark at six times the frequency of the measure/reference signal. This limits the
detection bandwidth helping to reject interfering signals from outside this bandwidth
improving the signal to noise ratio.
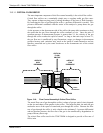
The IR Signal as the Photo-
Detector sees it after being
chopped by the GFC Wheel
S
CO REF
CO MEAS
Figure 13-6: Chopped IR Signal
06864B DCN6314