143
6. COMMUNICATIONS SETUP AND OPERATION
This instrument rear panel connections include an Ethernet port, a USB port (option) and
two serial communications ports (labeled RS232, which is the COM1 port, and COM2)
located on the rear panel (refer to Figure 3-4). These ports give the user the abilit
y to
communicate with, issue commands to, and receive data from the analyzer through an
external computer system or terminal.
This section provides pertinent information regarding communication equipment,
describes the instrument’s communications modes, presents configuration instructions
for the communications ports, and provides instructions for their use, including
communications protocol. Data acquisition is presented in Section 7.
6.1. DATA TERMINAL/COMMUNICATION EQUIPMENT (DTE DCE)
RS-232 was developed for allowing communications between data terminal equipment
(DTE) and data communication equipment (DCE). Basic terminals always fall into the
DTE category whereas modems are always considered DCE devices. The difference
between the two is the pin assignment of the Data Receive and Data Transmit functions.
• DTE devices receive data on pin 2 and transmit data on pin 3.
• DCE devices receive data on pin 3 and transmit data on pin 2.
To allow the analyzer to be used with terminals (DTE), modems (DCE) and computers
(which can be either), a switch mounted below the serial ports on the rear panel allows
the user to set the RS-232 configuration for one of these two data devices. This switch
exchanges the Receive and Transmit lines on RS-232 emulating a cross-over or null-
modem cable. The switch has no effect on COM2.
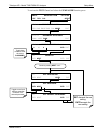
6.2. COMMUNICATION MODES, BAUD RATE AND PORT TESTING
Use the SETUP>MORE>COMM menu to configure COM1 (labeled RS232 on
instrument rear panel) and/or COM2 (labeled COM2 on instrument rear panel) for
communication modes, baud rate and/or port testing for correct connection. If using a
USB option communication connection, setup requires configuring the COM2 baud rate
(Section 6.2.2).
06864B DCN6314