Theory of Operation Teledyne API – Model T300/T300M CO Analyzer
298
I is the intensity with absorption.
L is the absorption path, or the distance the light travels as it is being absorbed.
C is the concentration of the absorbing gas; in the case of the T300/T300M, Carbon
Monoxide (CO).
α is the absorption coefficient that tells how well CO absorbs light at the specific
wavelength of interest.
13.2. MEASUREMENT FUNDAMENTALS
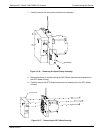
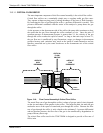
In the most basic terms, the T300/T300M uses a high-energy heated element to generate
a beam of broad-band IR light with a known intensity (measured during instrument
calibration). This beam is directed through multi-pass cell filled with sample gas. The
sample cell uses mirrors at each end to reflect the IR beam back and forth through the
sample gas a number of times (see Figure 13-1).
The total length that the reflected light travels is directly
related to the intended
sensitivity of the instrument. The lower the concentrations the instrument is designed to
detect, the longer the light path must be in order to create detectable levels of
attenuation.
Lengthening the absorption path is accomplished partly by making the physical
dimension of the reaction cell longer, but primarily by adding extra passes back and
forth along the length of the chamber.
Table 13-1: Absorption Path Lengths for T300 and T300M
MODEL
TOTAL NUMBER OF
REFLECTIVE PASSES
DISTANCE BETWEEN MIRRORS
TOTAL
ABSORPTION LIGHT
PATH
T300 32 437.5 mm 14 Meters
T300M 8 312.5 mm 2.5 Meters
06864B DCN6314