126
Operation selection function
Relationships between deviation and manipulated variable (output frequency)
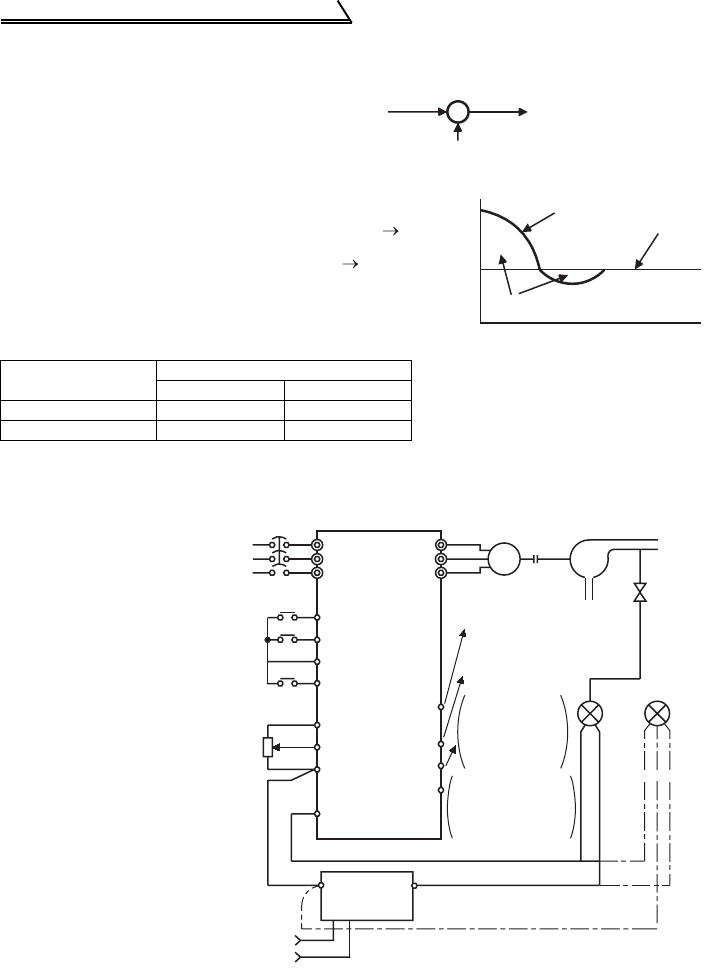
(3) Wiring example
5) Forward action
Increases the manipulated
variable (output frequency) if
deviation X = (set point -
measured value) is negative,
and decreases the manipulated
variable if deviation is positive.
Deviation
Positive Negative
Reverse action ÒÔ
Forward action ÔÒ
•
Pr. 62 = 14
•Pr. 64 = 15
•Pr. 65 = 16
•Pr. 88 = 20
*1. The power supply must be selected in accordance with the power specifications of
the detector used.
*2. The output signal terminals used depends on the Pr. 64, Pr. 65 settings.
*3. The input signal terminal used depends on the setting of Pr. 60 to Pr. 63.
*4. The contact input signal (AU Signal) need not be turned on.
Set point
X>0
X<0
Feedback signal
(Measured value)
+
-
[Cooling]
Too cold down
Hot up
Set point
Measured value
Deviation
Limit signal
common
For
2-wire
type
Detector
Motor
Power
supply
MCCB
Inverter
0
24V
power supply
(*1)
STF
STR
10
2
5
4
U
V
W
SE
(Measured value) 4 to 20mA
IM
P
-
+
++
-
A(RL)
C
RUN(FUP/FDN)
PID control
selection
RH(X14)(*3)
(*2)
Forward rotation
Reverse rotation
Setting
potentiometer
(Set point setting)
Pump
For
3-wire
type
Forward (reverse)
rotation output
signal common
AC1φ
200/220V 50/60Hz
(OUT)
(24V)
(COM)
Upper limit/
Lower limit
Forward
(reverse)
rotation
direction output
*4
SD
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3