244
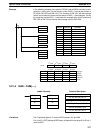
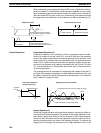
When overshooting is prevented with simple PID control, stabilization of distur-
bances is slowed (1). If stabilization of disturbances is speeded up, on the other
hand, overshooting occurs and response toward the target value is slowed (2).
With feed-forward PID control, there is no overshooting, and response toward
the target value and stabilization of disturbances can both be speeded up (3).
Simple PID Control Feed-forward PID control
As the target response is slowed,
the disturbance response worsens.
As the disturbance response is
slowed, the target response worsens.
Overshoot
Target response Disturbance response
(1)
(2)
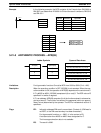
Control Operations Proportional Operation (P)
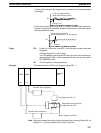
Proportional operation is an operation in which a proportional band is estab-
lished with respect to the set value (SV), and within that band the operation
amount (the control output amount) is made proportional to the deviation. If the
present value (PV) is smaller than the proportional band, the operation amount
will be 100%. If within the proportional band the operation amount is made pro-
portional to the deviation and gradually decreased until the SV and PV match
(i.e., until the deviation is 0), the operation amount will return to the previous val-
ue (forward operation).
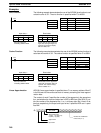
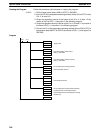
The proportional band is expressed as a percentage with respect to the total in-
put range. With proportional operation an offset (residual deviation) occurs, and
the offset is reduced by making the proportional band smaller. If it is made too
small, however, hunting will occur.
Proportional Operation
(Forward Operation)
Adjusting the Proportional Band
Operation
amount
SV
Proportional band
Proportional band too narrow (hunting occurring)
Proportional band just right
Proportional band too wide (large offset)
Offset
100%
0%
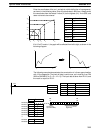
Integral Operation (I)
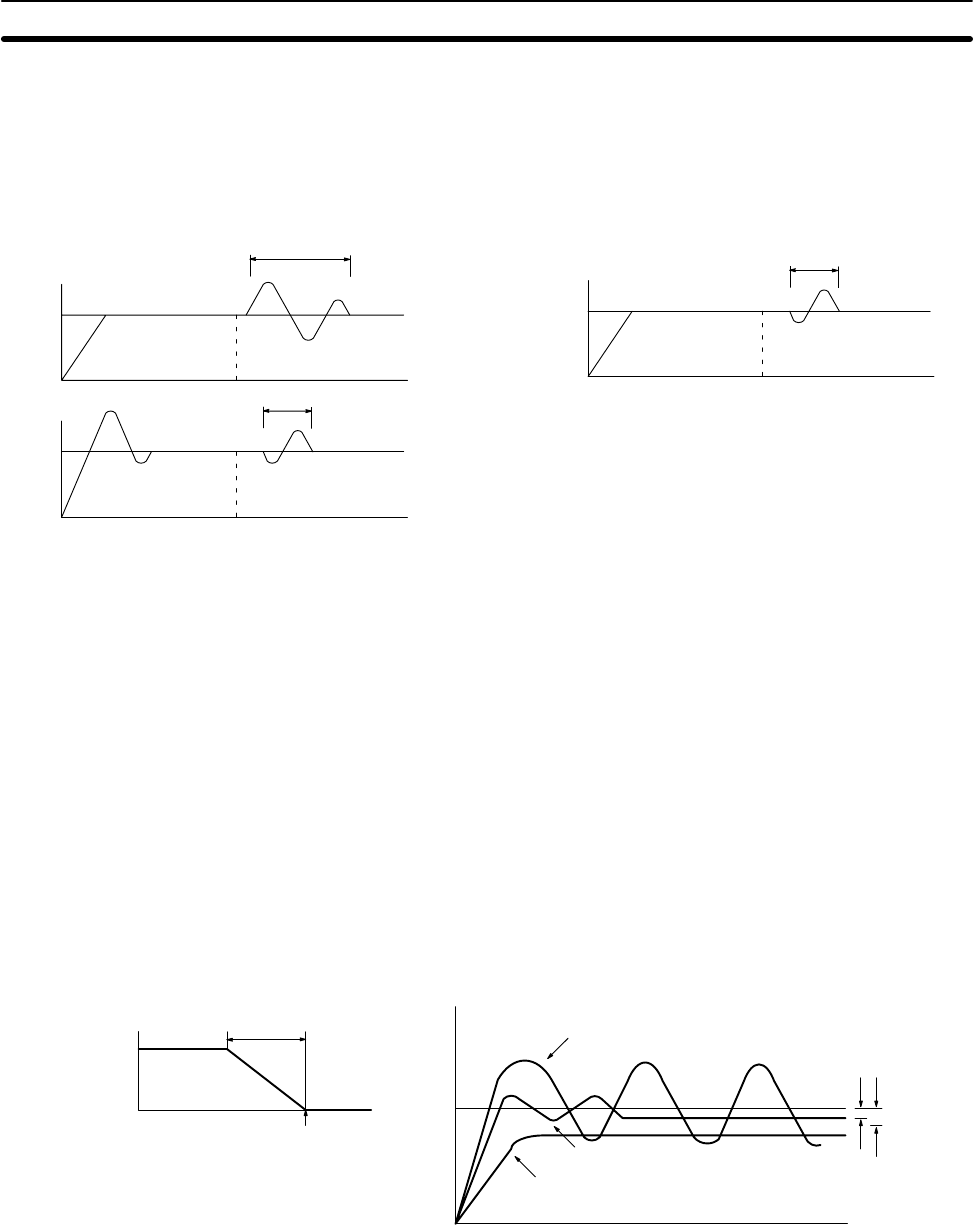
Combining integral operation with proportional operation reduces the offset ac-
cording to the time that has passed. The strength of the integral operation is indi-
cated by the integral time, which is the time required for the integral operation
amount to reach the same level as the proportional operation amount with re-
spect to the step deviation, as shown in the following illustration. The shorter the
integral time, the stronger the correction by the integral operation will be. If the
Special Math Instructions Section 5-21