233
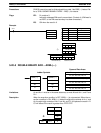
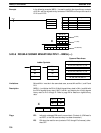
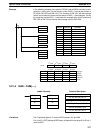
Example In the following example, DBSL(––) is used to divide the signed binary contents
of IR 002 and IR 001 with the signed binary contents of DM 0021 and DM 0020
and output the result to LR 24 through LR 21.
DBSL(––)
001
DM 0020
LR 21
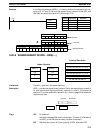
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 DBSL(––)
001
DM 0020
LR 21
00000
Dd: IR 001
B15C
Dr: DM 0020
001A
R: LR 21
DF7 0
R+1: LR 22
FFFA
(–8,736,420)
(26)
(–336,016 and –4/26)
Dd+1: IR 002
FF7A
Dr+1: DM 0021
0000
R+2: LR 23
FFFC
R+3: LR 24
FFFF
Remainder (–4) Quotient (–336,016)
5-21 Special Math Instructions
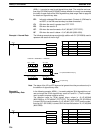
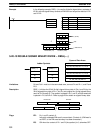
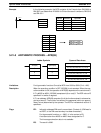
5-21-1 FIND MAXIMUM – MAX(––)
R
1
: First word in range
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR
C: Control data
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, LR
Ladder Symbols Operand Data Areas
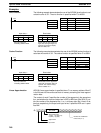
@MAX(––)
C
R
1
D
D: Destination word
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, LR
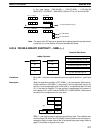
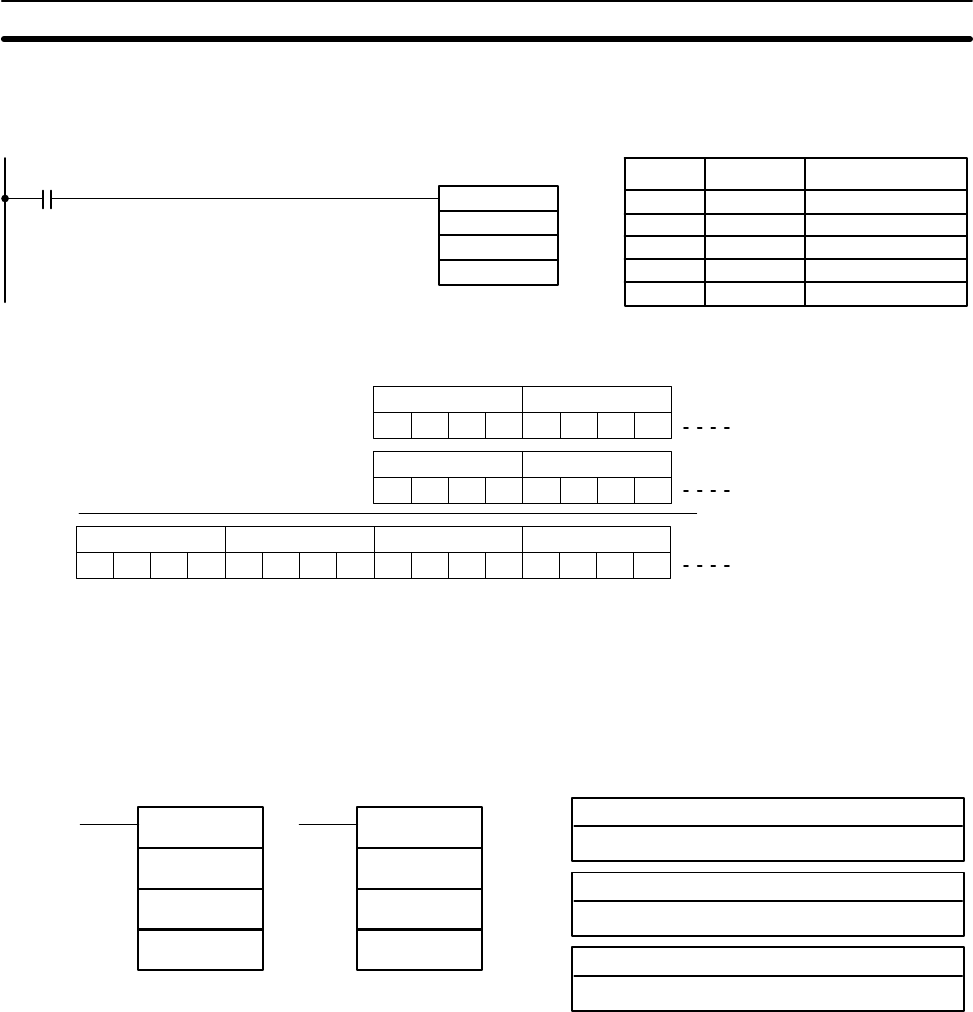
MAX(––)
C
R
1
D
Limitations N in C must be BCD between 001 to 999.
R
1
and R
1
+N–1 must be in the same data area.
Description When the execution condition is OFF, MAX(––) is not executed. When the exe-
cution condition is ON, MAX(––) searches the range of memory from R
1
to
R
1
+N–1 for the address that contains the maximum value and outputs the maxi-
mum value to the destination word (D).
If bit 14 of C is ON, MAX(––) identifies the address of the word containing the
maximum value in D+1. The address is identified differently for the DM area:
1, 2, 3...
1. For an address in the DM area, the word address is written to D+1. For ex-
ample, if the address containing the maximum value is DM 0114, then #0114
is written in D+1.
2. For an address in another data area, the number of addresses from the be-
ginning of the search is written to D+1. For example, if the address contain-
ing the maximum value is IR 114 and the first word in the search range is
IR 014, then #0100 is written in D+1.
Special Math Instructions Section 5-21