!
235
If bit 14 of C is ON and more than one address contains the same minimum val-
ue, the position of the lowest of the addresses will be output to D+1.
The number of words within the range (N) is contained in the 3 rightmost digits of
C, which must be BCD between 001 and 999.
When bit 15 of C is OFF, data within the range is treated as unsigned binary and
when it is ON the data is treated as signed binary. Refer to page 29 for details on
signed binary data.
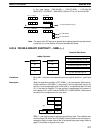
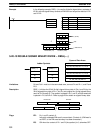
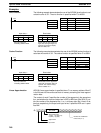
15 14 13 12 11 00
Data type
1 (ON): Signed binary
0 (OFF): Unsigned binary
Number of words
in range (N)
Not used – set to zero.
Output address to D+1?
1 (ON): Yes.
0 (OFF): No.
C:
Caution If bit 14 of C is ON, values above #8000 are treated as negative numbers, so the
results will differ depending on the specified data type. Be sure that the correct
data type is specified.
Flags ER: Indirectly addressed DM word is non-existent. (Content of :DM word is
not BCD, or the DM area boundary has been exceeded.)
The number of words specified in C is not BCD (000 to 999).
R
1
and R
1
+N–1 are not in the same data area.
EQ: ON when the minimum value is #0000.
5-21-3 AVERAGE VALUE – AVG(––)
S: Source word
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR
N: Number of cycles
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
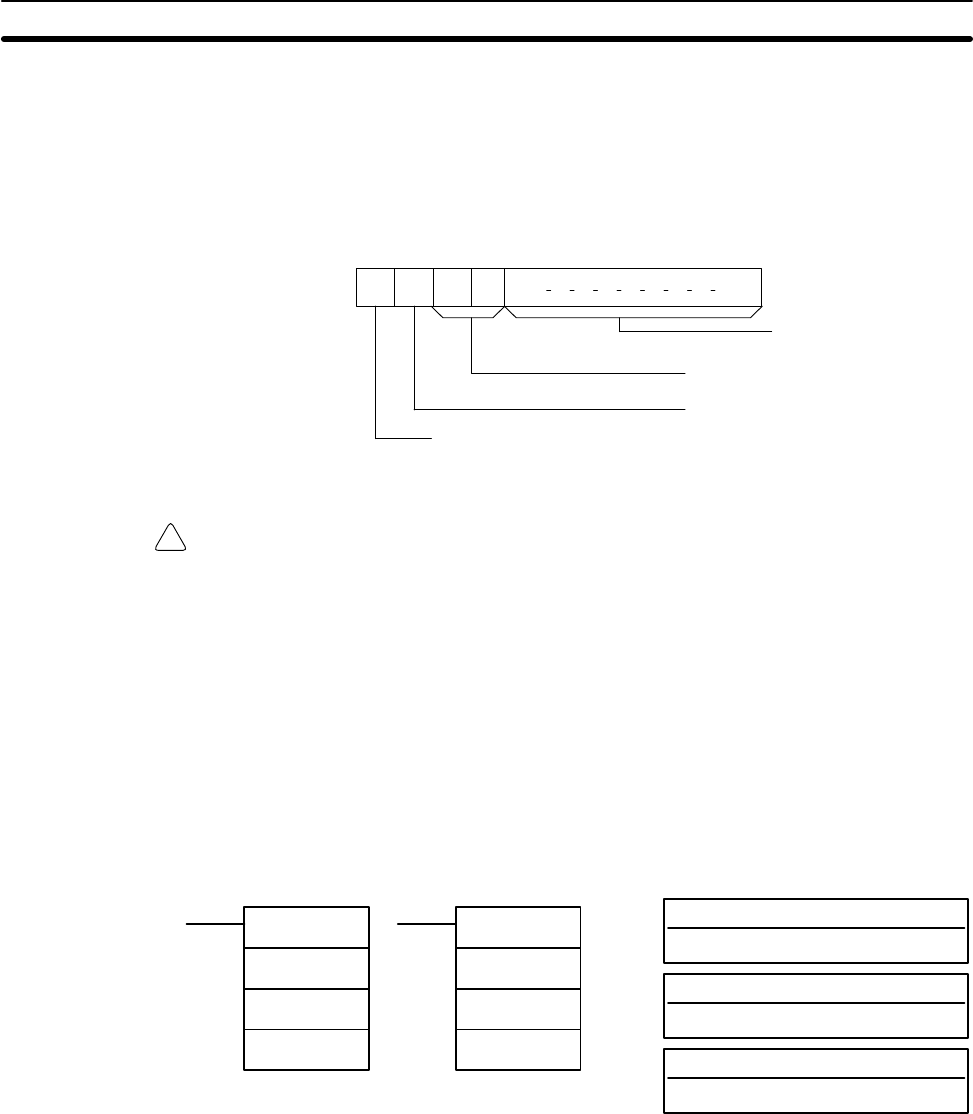
Ladder Symbols
Operand Data Areas
D: First destination word
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, LR
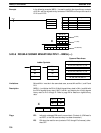
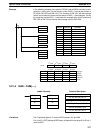
AVG(––)
S
N
D
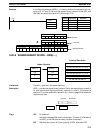
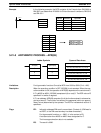
@AVG(––)
S
N
D
Limitations Data of S must be hexadecimal.
N must be BCD from #0001 to #0064.
D and D+N+1 must be in the same data area.
Description AVG(––) is used to calculate the average value of S over N cycles.
When the execution condition is OFF, AVG(––) is not executed.
For the first N–1 cycles when the execution condition is ON, AVG(––) writes the
value of S to D. Each time that AVG(––) is executed, the previous value of S is
stored in words D+2 to D+N+1. The first 2 digits of D+1 are incremented with
each execution and act as a pointer to indicate where the previous value is
stored. Bit 15 of D+1 remains OFF for the first N–1 cycles.
Special Math Instructions Section 5-21