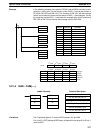
232
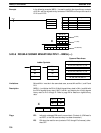
Example In the following example, DBS(––) is used to divide the signed binary contents of
IR 001 with the signed binary contents of DM 0020 and output the result to LR 21
and LR 22.
DBS(––)
001
DM 0020
LR 21
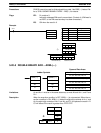
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 DBS(––)
001
DM 0020
LR 21
00000
Dd: IR 001
DDDA
Dr: DM 0020
001A
R: LR 21
FEB0
÷
R+1: LR 22
FFFA
(–8,742)
(26)
(–336 and –6)
Remainder (–6) Quotient (–336)
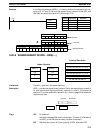
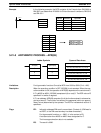
5-20-10 DOUBLE SIGNED BINARY DIVIDE – DBSL(––)
Dd: Dividend word (binary)
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
Dr: Divisor word (binary)
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
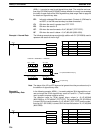
Ladder Symbols
Operand Data Areas
R: First result word
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR LR
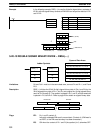
DBSL(––)
Dd
Dr
R
@DBSL(––)
Dd
Dr
R
Limitations Dd and Dd+1 must be in the same data area, as must Dr and Dr+1, and R and
R+3.
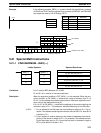
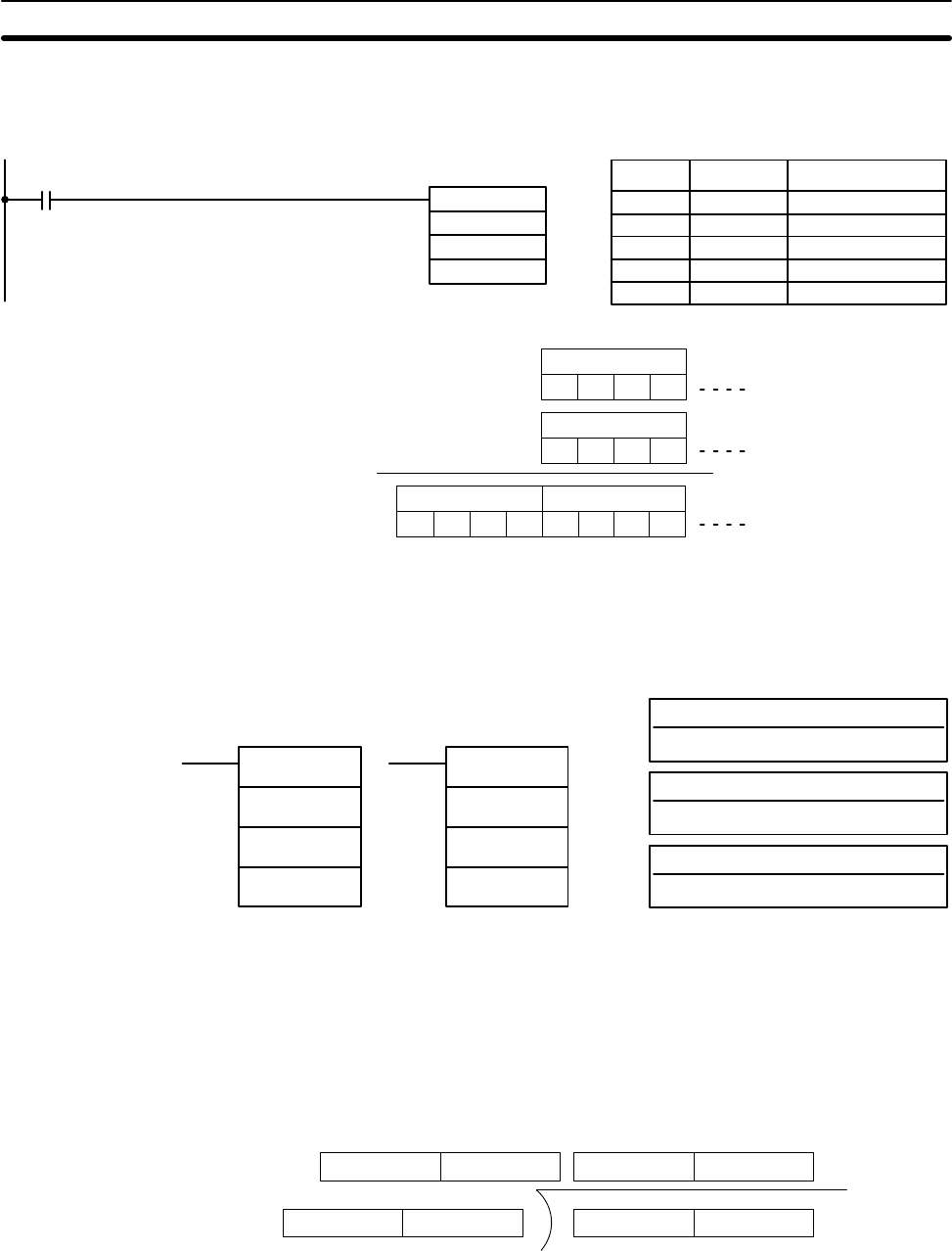
Description DBS(––) divides the 32-bit (8-digit) signed binary data in Dd+1 and Dd by the
32-bit signed binary data in Dr+1 and Dr, and outputs the 16-digit signed binary
result to R+3 through R. The quotient is placed in R+1 and R, and the remainder
is placed in R+3 and R+2. Refer to page 29 for details on signed binary data.
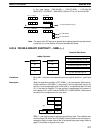
R+1 R
QuotientRemainder
Dd+1 DdDr+1 Dr
R+3 R+2
Flags ER: Dr+1 and Dr contain 0.
Indirectly addressed DM word is non-existent. (Content of :DM word is
not BCD, or the DM area boundary has been exceeded.)
EQ: ON when the content of R+1 and R (the quotient) is 0, otherwise OFF.
Binary Calculations Section 5-20