46 PI-MTE System Manual Version 4.C
Note: The start of the exposure is signaled by NOT SCAN going high but will not occur
until the current clean cycle and the additional user-defined number of cleans (typically 0)
have finished. "Number of Cleans" is defined on the Setup|Hardware
Setup|Cleans/Skips tab page. If you enter a value other than "0", you will further delay
the start of the exposure by that number of clean cycles.
Continuous Cleans
The Continuous Cleans function is provided when the start of an exposure is tied to an
external trigger (i.e., the experiment is being run in External Sync timing mode). The
continuous clean cycles are defined by the same parameter values as the standard clean
cycles. The difference is that continuous clean cycles occur between NOT SCAN going
high and External Sync going low. When the External Sync trigger arrives during a
continuous clean cycle, that cycle must be completed before the exposure will begin. In
time critical experiments, the number of rows per clean (set on the Hardware Setup|
Controller/Camera tab page) should be 1 or 2 to minimize the delay. Refer to "External
Sync with Continuous Cleans", page 55 for more information.
Readout
Introduction
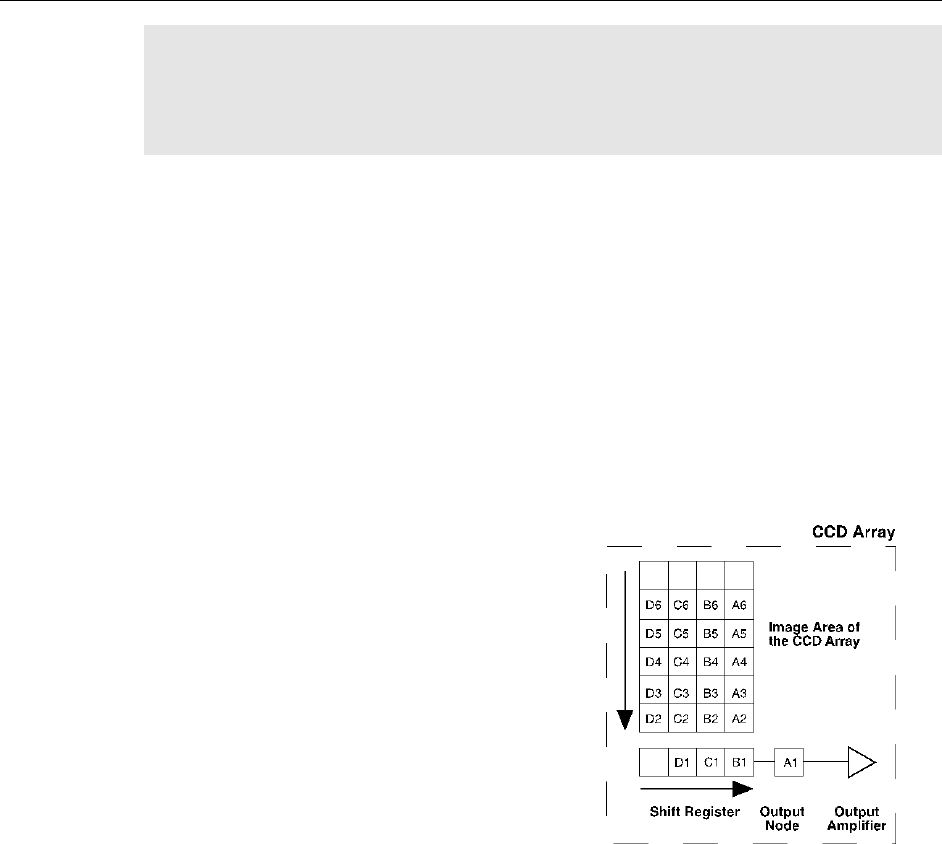
After the exposure time has elapsed, the charge
accumulated in the array pixels needs to be read
out of the array, converted from electrons to
digital format, and transmitted to the application
software where it can be displayed and/or
stored. Readout begins by moving charge from
the CCD image area to the shift register. The
charge in the shift register pixels, which
typically have twice the capacity of the image
pixels, is then shifted into the output node and
then to the output amplifier where the electrons
are grouped as electrons/count. This result
leaves the CCD and goes to the preamplifier
where gain is applied.
Figure 11. Array Terms for a CCD
with a Single Output Amplifier
WinView allows you to specify the type of readout (full frame or binned) and the gain
(the number of electrons required to generate an ADU).
Full Frame Readout
In this section, a simple 6 4 pixel CCD is used to demonstrate how charge is shifted
and digitized. Full frame readout, for full frame CCDs, reads out the entire CCD surface
at the same time.


















