71
10.
Step 7: Selection of Measuring Instruments
(1) Measuring instruments
Use measuring instruments with recommended pulse signals shown in the Table 10-1 below.
We also recommend using a watt-hour meter shown in the Table 10-2 below.
●● Make sure pulse unit is set in the measuring instruments. If not, consumption will
not be correctly measured, and charging functions and peak cut control will not
work correctly.
●● Power and gas consumption is counted by pulse. We will take no responsibility for
measurement results since they depend on performance and accuracy of
measuring instruments.
CAUTION
Table 10-1 Recommended pulse specification
Model name
Output pulse type
Output pulse width
Pulse unit
Description
Semi-conductor relay type
100 ~ 300ms (100ms or above)
Select a measuring instrument which outputs
non-voltage a-contact pulse per pulse output unit.
Watt-hour meter: 0.1kWh/pulse, 1kWh/pulse is recommended.
Water meter : m
3
/pulse
Gas meter : m
3
/pulse
Calorimeter : MJ/pulse
* Except for the watt-hour meter, select the measuring
instrument type with the appropriate pulse unit.
ON
100ms ~ 300ms
Table 10-2 Recommended watt-hour meter
Model name
Maker
Model name
Others
Description
Mitsubishi Electric
Single-phase 2 wire system
Single-phase 3 wire system, three-phase 3 wire system
Up to 32 units of Watt-hour meter can be used per 1 unit of PLC.
* (H) means it comes with a transformer (CT); (V) means it is semi-flush mounted with rear connection.
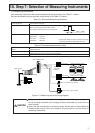
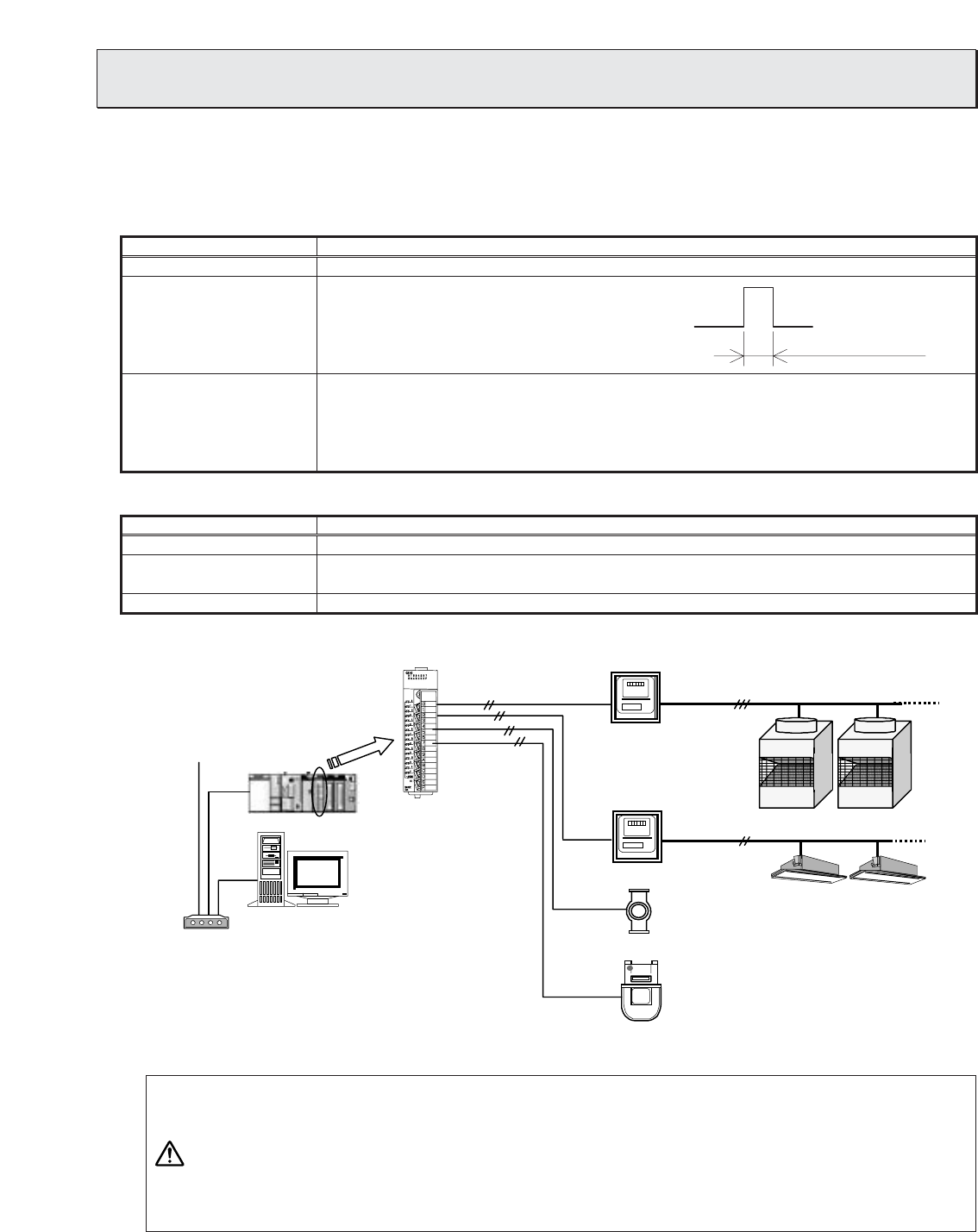
Gas meter with a pulse oscillator
PLC DI board (QX40)
TG-2000A
Other systems
PLC (with a pulse count software)
Three-phase
Watt-hour meter
with a pulse
oscillator
Outdoor unit power supply
Single-phase Indoor unit power supply
Water meter with a pulse oscillator
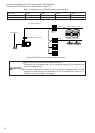
Figure 10-1 Measuring instrument wiring diagram