523
FX3S/FX3G/FX3GC/FX3U/FX3UC Series
Programming Manual - Basic & Applied Instruction Edition
18 Floating Point – FNC110 to FNC139
18.21 FNC133 – ASIN / Floating Point Arc Sine
11
FNC30-FNC39
Rotation and
Shift
12
FNC40-FNC49
Data Operation
13
FNC50-FNC59
High-Speed
Processing
14
FMC60-FNC69
Handy
Instruction
15
FNC70-FNC79
External FX I/O
Device
16
FNC80-FNC89
External FX
Device
17
FNC100-FNC109
Data
Transfer 2
18
FNC110-FNC139
Floating Point
19
FNC140-FNC149
Data
Operation 2
20
FNC150-FNC159
Positioning
Control
Program example
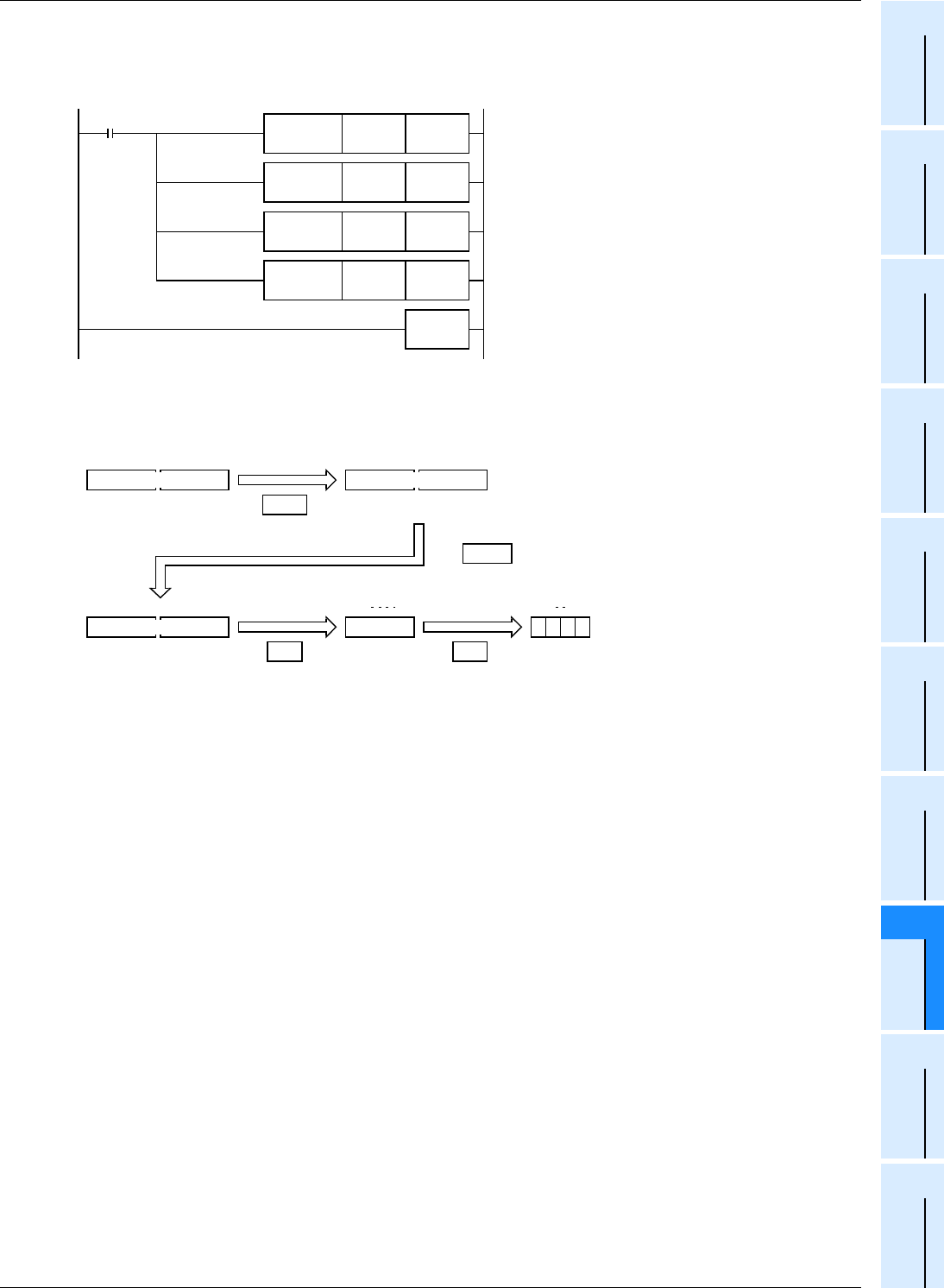
In the program example shown below, the SIN
−1
value of data (binary floating point) stored in D0 and D1 is calculated,
and the angle is output in 4-digit BCD to Y040 to Y057 when X000 turns ON.
Operation when "0.5" is stored in D0 and D1
The angle (in radians) is calculated by the SIN
−
1
operation ([1]).
The value in radians is converted into the value in
degrees ([2]).
The angle expressed in binary floating point (real
number) is converted into an integer (binary) ([3]).
X000
FNC137
DDEG
D10 D20
FNC133
DASIN
D0 D10
FNC129
INT
D20 D30
END
The angle expressed in integer (binary) is output to
the display unit ([4]).
FNC 18
BCD
D30 K4Y40
Binary floating point
(real number) value
0.5
D1 D0
[1]
Conversion
by SIN
−
1
operation
Binary floating point
(real number) value
0.5235988
D11 D10
DASIN
Binary floating point
(real number) value
30
D21 D20
[3]
Conversion
into binary
30
b15 b0
D30
Binary
value
[4] BCD
operation
BCD
0 0 3 0
Y057 Y040
BCD
value
DDEG
[2] Conversion into degrees
INT


















