DMC-1700/1800 Appendices • 235
The vector distance is the integral of Vs, or the total distance traveled along the path. To illustrate this further,
suppose that a string was placed along the path in the X-Y plane. The length of that string represents the distance
traveled by the vector motion.
The vector velocity is specified independently of the path to allow continuous motion. The path is specified as a
collection of segments. For the purpose of specifying the path, define a special X-Y coordinate system whose origin
is the starting point of the sequence. Each linear segment is specified by the X-Y coordinate of the final point
expressed in units of resolution, and each circular arc is defined by the arc radius, the starting angle, and the angular
width of the arc. The zero angle corresponds to the positive direction of the X-axis and the CCW direction of
rotation is positive. Angles are expressed in degrees, and the resolution is 1/256
th
of a degree. For example, the path
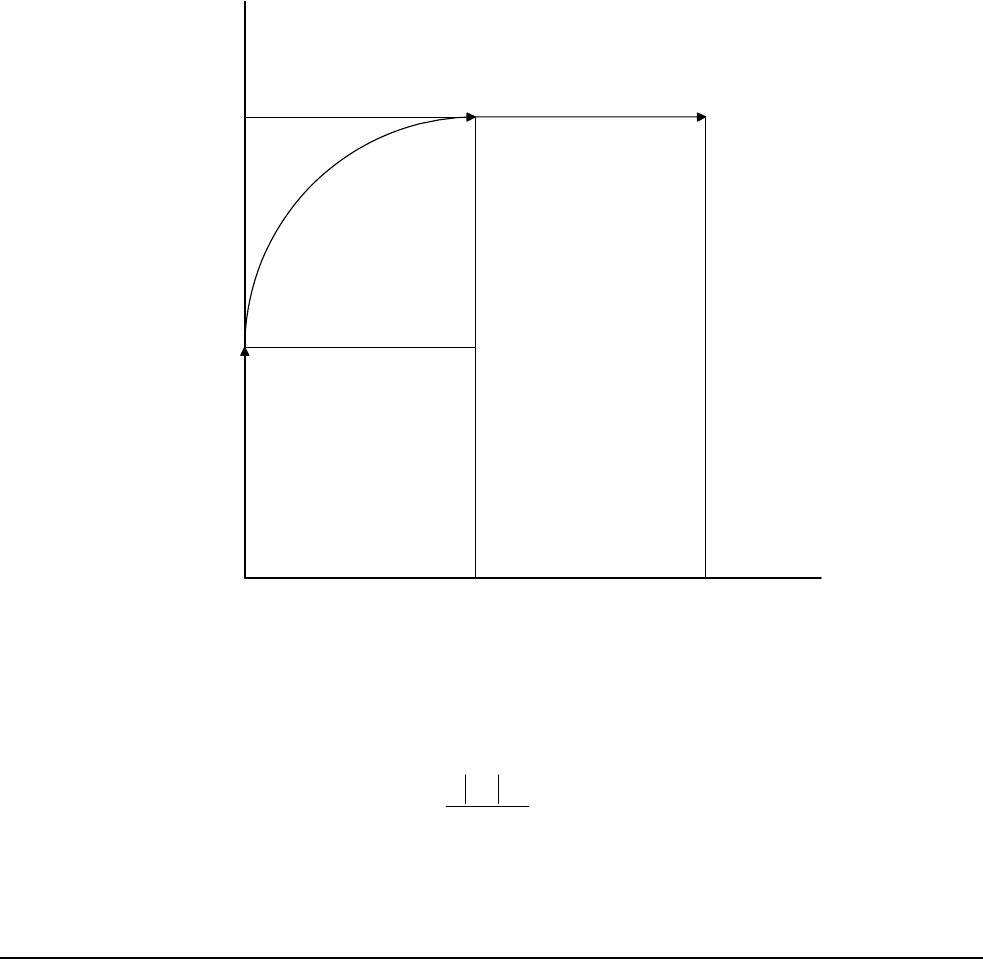
shown in Fig. A.13 is specified by the instructions:
VP 0,10000
CR 10000, 180, -90
VP 20000, 20000
10000 20000
20000
10000
Y
CD
B
A
X
Figure A.13 - X-Y Motion Path
The first line describes the straight line vector segment between points A and B. The next segment is a circular arc,
which starts at an angle of 180° and traverses -90°. Finally, the third line describes the linear segment between
points C and D. Note that the total length of the motion consists of the segments:
A-B Linear 10000 units
B-C Circular
R
Δ
θ
π
2
360
= 15708
C-D Linear 10000