DMC-1700/1800 Chapter 7 Application Programming • 169
JP #Loop Repeat
EN End
Example - Position Follower (Continuous Move)
Method: Read the analog input, compute the commanded position and the position error. Command the motor to
run at a speed in proportions to the position error
.
INSTRUCTION INTERPRETATION
#Cont Label
AC 80000;DC 80000 Acceleration rate
JG 0 Start job mode
BGX Start motion
#Loop
VAR=@AN[1]*1000 Compute desired position
VER=VAR-_TPX Find position error
VEL=VER*20 Compute velocity
JG VEL Change velocity
JP #Loop Change velocity
EN End
Example Applications
Wire Cutter
An operator activates a start switch. This causes a motor to advance the wire a distance of 10”. When the motion
stops, the controller generates an output signal which activates the cutter. Allowing 100 ms for the cutting
completes the cycle.
Suppose that the motor drives the wire by a roller with a 2” diameter. Also assume that the encoder resolution is
1000 lines per revolution. Since the circumference of the roller equals 2π inches, and it corresponds to 4000
quadrature, one inch of travel equals:
4000/2π = 637 count/inch
This implies that a distance of 10 inches equals 6370 counts, and a slew speed of 5 inches per second, for example,
equals 3185 count/sec.
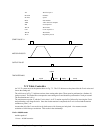
The input signal may be applied to I1, for example, and the output signal is chosen as output 1. The motor velocity
profile and the related input and output signals are shown in Fig. 7.1.
The program starts at a state that we define as #A. Here the controller waits for the input pulse on I1. As soon as
the pulse is given, the controller starts the forward motion.
Upon completion of the forward move, the controller outputs a pulse for 20 ms and then waits an additional 80 ms
before returning to #A for a new cycle.
INSTRUCTION FUNCTION
#A Label