12-14
Cisco ONS 15454 Reference Manual, R8.5.x
78-18106-01
Chapter 12 SONET Topologies and Upgrades
12.3 Path Protection
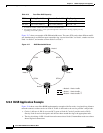
Figure 12-12 Connecting Fiber to a Four-Node, Four-Fiber BLSR
12.3 Path Protection
Path Protection Configurations(PPC) provide duplicate fiber paths around the ring. Working traffic flows
in one direction and protection traffic flows in the opposite direction. If a problem occurs with the
working traffic path, the receiving node switches to the path coming from the opposite direction.
CTC automates ring configuration. path protection traffic is defined within the ONS 15454 on a
circuit-by-circuit basis. If a path-protected circuit is not defined within a 1+1 or BLSR line protection
scheme and path protection is available and specified, CTC uses path protection as the default.
A path protection circuit requires two DCC-provisioned optical spans per node. Path protection circuits
can be created across these spans until their bandwidth is consumed.
Note If a path protection circuit is created manually by TL1, data communications channels (DCCs) are not
needed; therefore, path protection circuits are limited by the cross-connection bandwidth or the span
bandwidth, but not by the number of DCCs.
The span bandwidth consumed by a path protection circuit is two times the circuit bandwidth, because
the circuit is duplicated. The cross-connection bandwidth consumed by a path protection circuit is three
times the circuit bandwidth at the source and destination nodes only. The cross-connection bandwidth
consumed by an intermediate node has a factor of one.
61958
Node 1
West East
West East
West East
West East
Slot
5
Slot
12
Node 4
Slot
5
Slot
12
Node 2
Slot
5
Slot
12
Node 3
Slot
5
Slot
12
Tx
Rx
Slot
6
Slot
13
Tx
Rx
Slot
6
Slot
13
Tx
Rx
Slot
6
Slot
13
Tx
Rx
Slot
6
Slot
13
Working fibers
Protect fibers