279
Programming Appendix A
Instruction Variations
The following variations are available for instructions to differentiate executing conditions.
Input Conditions
The FQM1 offers the following types of basic and special instructions.
• Non-differentiated instructions executed every cycle
• Differentiated instructions executed only once
Non-differentiated Instructions
• Output instructions that require input conditions are executed once every cycle while the input condition is
valid (ON or OFF).
• Input instructions that create logical starts and intermediate instructions that read bit status, make compar-
isons, test bits, or perform other types of processing every cycle. If the results are ON, power flow is output
(i.e., the input condition is turned ON).
Input-differentiated Instructions
• Upwardly Differentiated Instructions (Instructions Preceded by @)
• Output Instructions: The instruction is executed only during the cycle in which the input condition
turns ON (OFF
→ ON) and are not executed in the following cycles.
• Input Instructions (Logical Starts and Intermediate Instructions): The instruction reads bit status,
makes comparisons, tests bits, or perform other types of processing every cycle and will output an ON
execution condition (power flow) when results switch from OFF to ON. The execution condition will turn
OFF the next cycle.
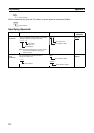
Variation Symbol Description
Differentiation ON @ Instruction that differentiates when the input condition turns ON.
OFF % Instruction that differentiates when the input condition turns OFF.
MOV@
Instruction (mnemonic)
Differentiation variation
MOV
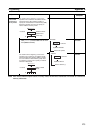
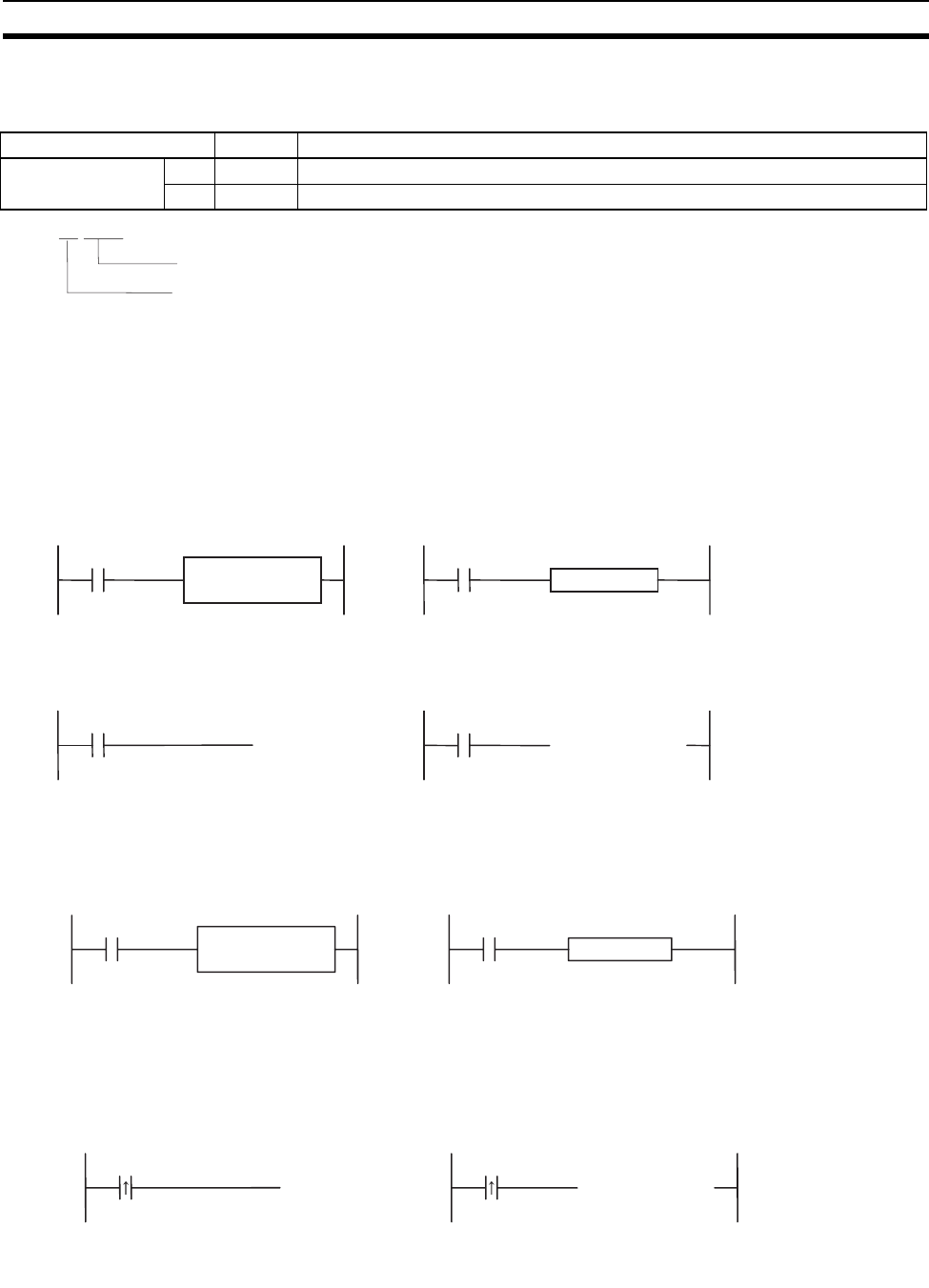
Example
Non-differentiated
output instruction
Example
Non-differentiated input instruction
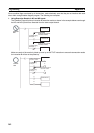
@MOV
0001.02
Example
Executes the MOV instruction once when
CIO 0001.02 goes OFF → ON.
(@) Upwardly differ
entiated instruction
0001.03
Example
Upwardly differentiated input instruction
ON execution condition created for one
cycle only when CIO 0001.03 goes from
OFF to ON.