25
Example of equipment selection
The following shows an example of equipment selection based upon a building model.
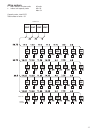
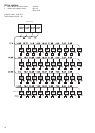
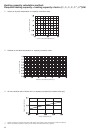
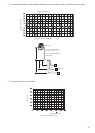
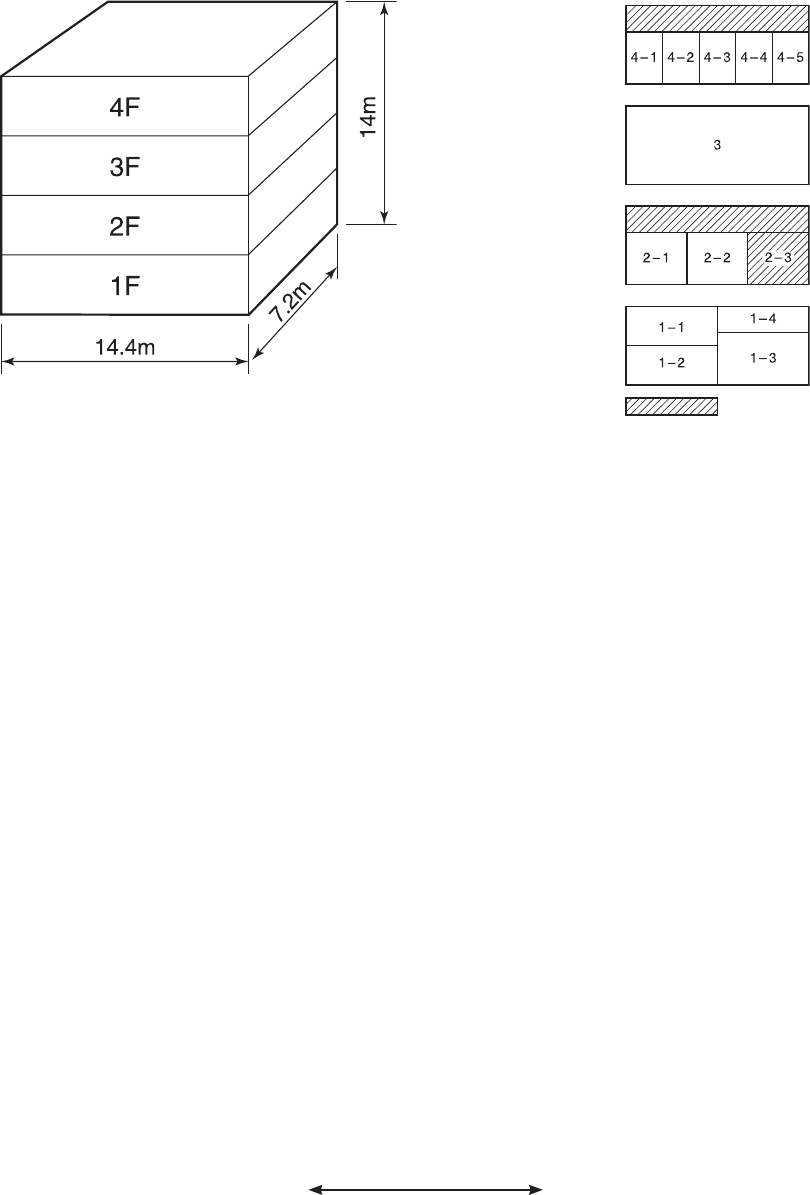
Fig. 1 - Overview of building model
Outside view Floor configuration
Non-air conditioning zone
• Steel frame, reinforced concrete building, four floors
above ground. Total floor area : 415 m²
Outdoor unit is installed on the roof.
• Indoor design conditions:
Cooling: 27.0/19.0°C db/wb. Heating: 20°C db
• Outdoor design conditions:
Cooling: 35°C db (standard condition). Heating: 3°C wb (standard condition: 6°C wb)
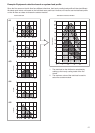
Selection criteria for each floor
1F: Outdoor unit capacity exactly matches the total indoor unit capacity.
Total indoor unit hp = Outdoor unit hp Indoor: 2.5 hp x 2 units + 3.2 hp + 2 hp = 10.2 hp
Outdoor: 10 hp Same capacity
2F: Outdoor unit capacity matches the potential total indoor unit capacity with the possibility of future
extension.
Office rooms 2 and 3 are to be used as warehouses at first, so air conditioning is not necessary at present.
However, there is a plan to convert them into offices, so an outdoor module with extra capacity is required.
Piping/wiring are carried out. Indoor unit is not yet installed.
When the rooms are used as an office later, the indoor unit is installed.
3F: One indoor unit is connected to one outdoor unit.
The outdoor module should have sufficient capacity to cover the peak demand of the indoor unit connected.
4F: Consider the diversity factor and have the outdoor module match 135% of indoor unit capacity.
This is a typical matching of indoor/outdoor units for a Super MMS system.
• Total indoor unit hp > Outdoor unit hp
• Select each indoor unit based on individual peak room load.
Indoor: 2.5 hp + 2.5 hp + 2 hp + 2 hp (capacity difference in each room) + 1.3 hp =
10.3 hp (different capacity) Outdoor: 8 hp (different capacity)
• The cooling load profile needs to be taken into consideration.
Small meeting room
Executive rooms
Office rooms
(Entire floor)
Office rooms
Stores