DMC-1700/1800 Chapter 10 Theory of Operation • 185
Chapter 10 Theory of Operation
Overview
The following discussion covers the operation of motion control systems. A typical motion control system consists
of the elements shown in Fig 10.1.
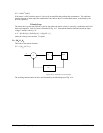
COMPUTER CONTROLLER DRIVER
MOTORENCODER
Figure 10.1 - Elements of Servo Systems
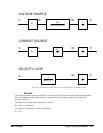
The operation of such a system can be divided into three levels, as illustrated in Fig. 10.2. The levels are:
1. Closing the Loop
2. Motion Profiling
3. Motion Programming
The first level, the closing of the loop, assures that the motor follows the commanded position. This is done by
closing the position loop using a sensor. The operation at the basic level of closing the loop involves the subjects of
modeling, analysis, and design. These subjects will be covered in the following discussions.
The motion profiling is the generation of the desired position function. This function, R(t), describes where the
motor should be at every sampling period. Note that the profiling and the closing of the loop are independent
functions. The profiling function determines where the motor should be and the closing of the loop forces the motor
to follow the commanded position
The highest level of control is the motion program. This can be stored in the host computer or in the controller.
This program describes the tasks in terms of the motors that need to be controlled, the distances and the speed.