SetupTeledyne API – Model T300/T300M CO Analyzer
Teledyne Analytical Instruments 127
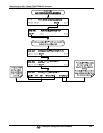
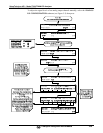
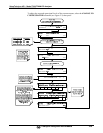
5.9.3.7. MANUAL ADJUSTMENT OF CURRENT LOOP OUTPUT SPAN AND
OFFSET
A current loop option may be purchased for the A1, A2 and A3 analog outputs of the
analyzer. This option places circuitry in series with the output of the D-to-A converter
on the motherboard that changes the normal DC voltage output to a 0-20 milliamp signal
(see Section 3.3.1.4).
The outputs can be ordered scaled to any set of limits within that 0-20 mA
range, however most current loop applications call for either 0-20 mA or 4-
20 mA range spans.
All current loop outputs have a +5% over range. Ranges whose lower limit
is set above 1 mA also have a –5% under range.
To switch an analog output from voltage to current loop, follow the instructions in
Section 5.9.3.1 (select CURR from the list of options on the “Output Range” menu).
Adjusting the signal zero and span levels of the current loop output is done by raising or
lowering the voltage output of the D-to-A converter circuitry on the analyzer’s
motherboard. This raises or lowers the signal level produced by the current loop option
circuitry.
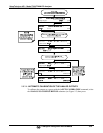
The software allows this adjustment to be made in 100, 10 or 1 count increments. Since
the exact amount by which the current signal is changed per D-to-A count varies from
output-to-output and instrument-to-instrument, you will need to measure the change in
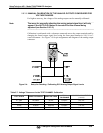
the signal levels with a separate, current meter placed in series with the output circuit.
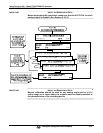
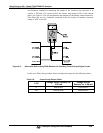
See Figure 3-9 for pin assignments and diagram of the analog output connector.
Figure 5-5: Setup for Checking / Calibration Current Output Signal Levels Using an Ammeter
CAUTION
GENERAL SAFETY HAZARD
Do not exceed 60 V peak voltage between current loop outputs and instrument ground.