Instruction Manual
IM-106-5500, Original Issue
August 2005
CCO 5500
1-6
Calculation Sequence The calculations for one complete operating cycle of the instrument are given
below:
•measure D1 & D2
• measure E1 & E2
• compute Y
• smooth Y
• linearize and correct for path length
• normalize measurement
• smooth to produce final gas outputs
Normalization Equations Normalization of data collected by the analyses is essential to compare
emission levels of pollutants into the atmosphere. Software in Rosemount
Analyzers perform all calculations and provides results in various units, vpm,
mg/m
3
and mg/Nm
3
; derivation of these results is described in this section.
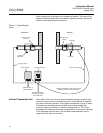
CCO 5500 CO analyzers are cross-duct type and thus measure the quantity
(or number of molecules) of gas within their sight path. This measurement is
converted into a concentration which is fully compensated for the expansion
effects of temperature, while assuming constant atmospheric pressure. This
basic measurement is referred to as 'ppm' (parts per million). However, to
obtain a true concentration 'vpm' (ppm by volume) the 'ppm' value must be
normalized for pressure using the following expression.
Correction to standard pressure -
where standard pressure is taken as 101 kPascals.
The next stage in the process is to determine the mass concentration. The
conversion at STP uses conversion factors determined as follows:
Conversion to mass concentration -
The conversion factor given below:
Conversion factors (N) -
The mass concentration present is calculated as below:
mg/m
3
(STP) = N. vpm
This value is the mass concentration of the gas at STP.
Correction for oxygen and water vapor.
Finally the effects of water vapor and oxygen need to be considered.
vpm = ppm x standard pressure (abs)
measured pressure (abs)
N=RMM
V
where N = conversion factor
RMM = relative molecular mass of the gas
V = 22.4 (standard volume of an ideal gas)
Molecular mass (RMM) = 12 + 16 = 28
1 vpm = 28/22.4 = 1.25 mg/m
3