Teledyne API – Technical Manual - Model 300E Family CO Analyzers Troubleshooting & Repair
287
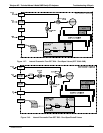
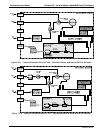
13.4.2. EXCESSIVE NOISE
Noise is continuously monitored in the TEST functions as the STABIL reading and only becomes meaningful
after sampling a constant gas concentration for at least 10 minutes. Compare the current STABIL reading with
that recorded at the time of manufacture (included in the M300E/EM
Final Test and Validation Data Sheet,P/N
04271 shipped with the unit from Teledyne API).
1. The most common cause of excessive noise is leaks. Leak check and flow check the instrument
described in Section 12.3.3 and 12.3.4.
2.
Dete
ctor failure – caused by failure of the hermetic seal or over-temperature due to poor heat sinking of
the detector can to the optical bench.
In addition to increased noise due to poor signal-to-noise ratio, another indicator of detector failure is
a drop in the signal levels of the CO MEASURE signal and CO REFERENCE signal.
3. Sync/Demod Board failure. There are many delicate, high impedance parts on this board. Check the
CO MEAS and CO REF Test Functions via the Front Panel Display.
4. The detector cooler control circuit can fail for reasons similar to the detector itself failing. Symptoms
would be a change in MR RATIO Test Function when zero air is being sampled.
5. Also check the SIGNAL I/O parameter PHT DRIVE.
After warm-up, and at 25
o
C ambient, if PHT DRIVE < 4800 mV, the cooler is working properly.
If PHT DRIVE is > 4800 mV there is a malfunction.
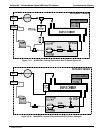
6. The +5 and 15 VDC voltages in the M300E/EM are provided by switching power supplies.
Switch mode supplies create DC outputs by switching the input AC waveform at high frequencies.
As the components in the switcher age and degrade, the main problem observed is increased noise
on the DC outputs.
If a noisy switcher power supply is suspected, attach an oscilloscope to the DC output test points
located on the top right hand edge of the Relay board.
Look for short period spikes > 100 mV p-p on the DC output.
04288D DCN5752