Theory of Operation Teledyne API – Technical Manual - Model 300E Family CO Analyzers
234
11.3. PNEUMATIC OPERATION
CAUTION
GENERAL SAFETY HAZARD
It is important that the sample airflow system is both leak tight and not pressurized
over ambient pressure.
Regular leak checks should be performed on the analyzer as described in the
maintenance schedule, Table 12-1.
Procedures for correctly performing leak checks can be found in Section 12.3.3.
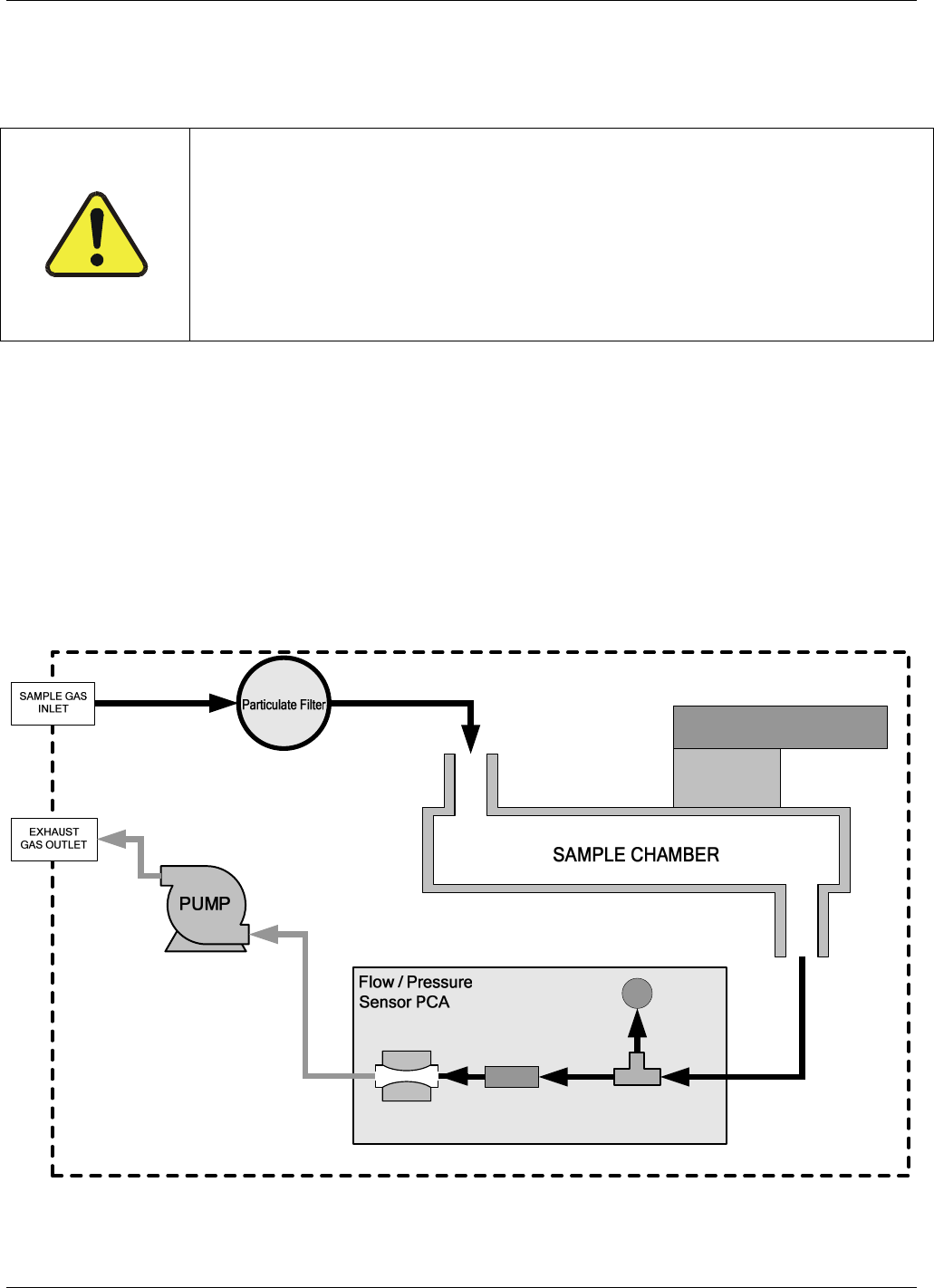
An internal pump evacuates the sample chamber creating a small vacuum that draws sample gas into the
analyzer. Normally the analyzer is operated with its inlet near ambient pressure either because the sample is
directly drawn at the inlet or a small vent is installed at the inlet. There are several advantages to this “pull
through” configuration.
By placing the pump down stream from the sample chamber several problems are avoided.
First the pumping process heats and compresses the sample air complicating the measurement process.
Additionally, certain physical parts of the pump itself are made of materials that might chemically react with
the sample gas.
Finally, in certain applications where the concentration of the target gas might be high enough to be
hazardous, maintaining a negative gas pressure relative to ambient means that should a minor leak occur,
no sample gas will be pumped into the atmosphere surrounding analyzer.
INSTRUMENT CHASSIS
SAMPLE
PRESSURE
SENSOR
FLOW
SENSOR
Sample Gas
Flow Control
GFC Wheel
Housing
GFC Motor Heat Sync
Figure 11-7: Internal Pneumatic Flow – Basic Configuration
04288D DCN5752