6.8 CALIBRATING AN IN-SERVICE SENSOR — CONDUCTIVITY
6.8.1 Purpose
1. After a conductivity sensor has been in service for a
period of time, recalibration may be necessary.
2. There are three ways to calibrate a sensor.
a. Use a standard instrument and sensor to
measure the conductivity of the process stream.
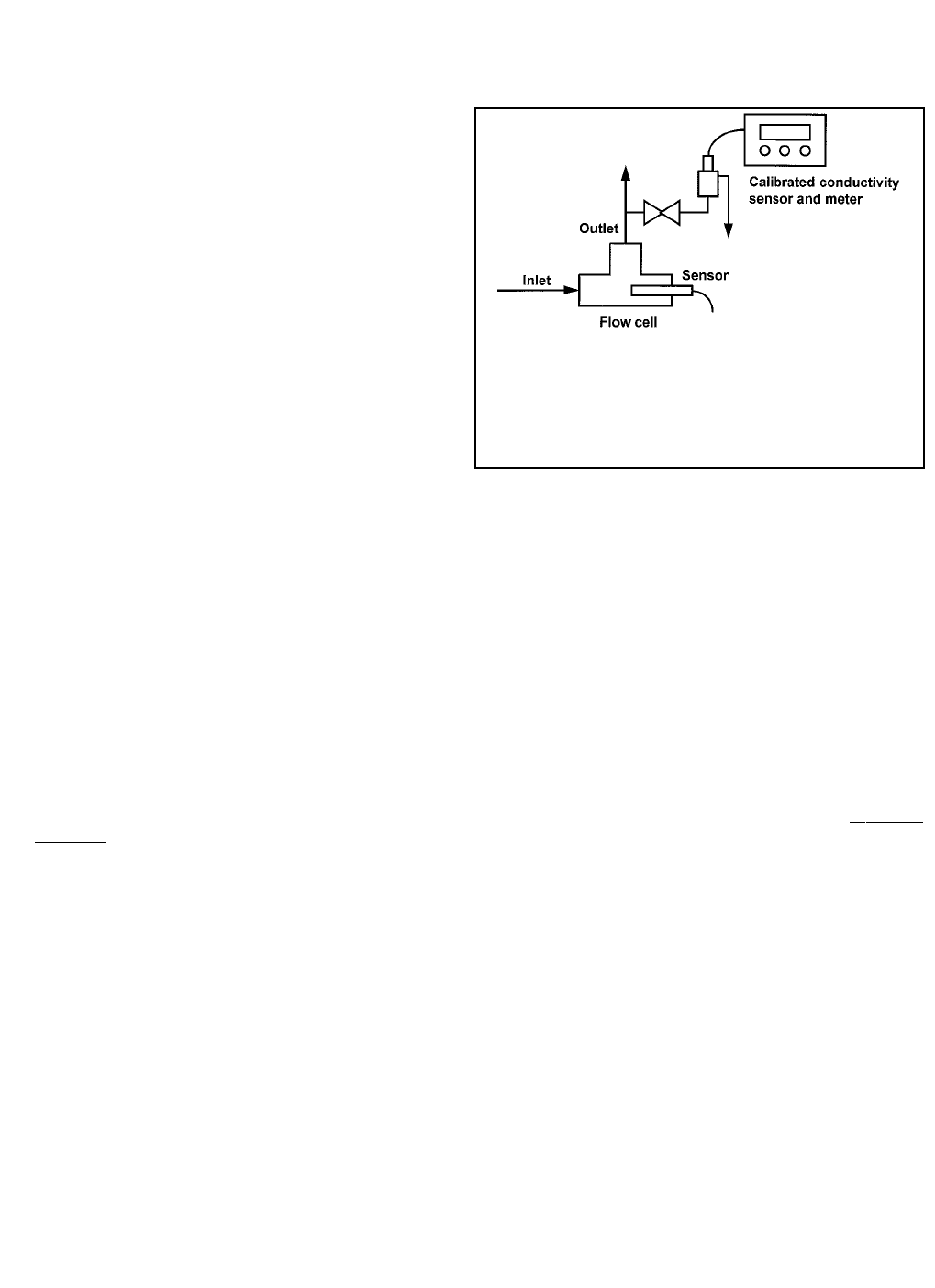
It is not necessary to remove the sensor from
the process piping. See Figure 6-2. The temper-
ature correction used by the standard instru-
ment may not exactly match the temperature
correction used by the Solu Comp II. To avoid
errors, turn off temperature correction in the
both the analyzer and the standard instru-
ment.
b. Place the sensor in a solution of known conduc-
tivity and make the analyzer reading match the
conductivity of the standard solution. Use this
method if the sensor can be easily removed from the process piping and a standard is available. Be care-
ful using standard solutions having conductivity less than 100 µS/cm. Low conductivity standards are high-
ly susceptible to atmospheric contamination. Avoid calibrating sensors with 0.01/cm cell constants against
conductivity standards in the range 100 to 300 µS/cm. The resistance of these solutions may be too low
for an accurate measurement. Calibrate sensors with 0.01/cm cell constant using method c. For addition-
al information, see ASTM D5391.
c.
To calibrate a 0.01/cm sensor
, check it against a standard instrument and 0.01/cm
sensor
while both
sen-
sor
s are measuring water having a conductivity between 5 and 10 µS/cm. To avoid drift caused by absorp-
tion of atmospheric carbon dioxide, saturate the sample with air before making the measurements.
FIGURE 6-2. Calibration Against a Standard Cell
To ensure adequate flow past the sensor during calibration,
take the sample downstream from the sensor. For best
results, use a flow-through standard cell. If the process tem-
perature is much different from ambient, keep connecting
lines short and insulate the flow cell.
MODEL SOLU COMP II SECTION 6.0
CALIBRATION
4. Turn off temperature correction.
6.8.2 Procedure-Calibration against a standard meter and cell
1. Calibration against a standard meter and cell transfers the calibration of the standard instrument to the
process instrument.
2. Calibrate the standard meter and cell using an accepted procedure, for example ASTM D 1125, S
tandard
Methods 2510, or equivalent. A portable, calibrated standard meter and cell is available from Rosemount
Analytical (Model Number 1055C-01-99SQ SQ6053).
3. Most conductivity instruments automatically correct measured conductivity to the value at 25°C. Different
instruments may apply slightly different temperature corrections. To avoid errors during calibration, turn off
automatic temperature correction in both the analyzer and the standard meter.
NOTE
If a portable reference meter is not available and the conductivity of the grab sample must
be determined in the laboratory, temperature correction in both the Solu Comp II and the
laboratory instrument MUST REMAIN ON. Be sure that the reference instrument and the
Solu Comp II are applying the same temperature correction.
55


















