32
MODEL SOLU COMP II SECTION 5.0
PROGRAMMING THE ANALYZER
5.3 CONFIGURING AND RANGING THE OUTPUTS.
5.3.1 Purpose
The Solu Comp II accepts input from a pH, ORP, or conductivity sensor and has two current outputs. This section
describes how to configure and range the outputs. CONFIGURE THE OUTPUTS FIRST.
1. Configuring an output means
a. Selecting either a 4-20 mA or 0-20 mA output,
b. Assigning a sensor and a measurement (pH, ORP, redox potential, conductivity, resistivity, or total dis-
solved solids [TDS]) to output 1 and output 2,
c. Turning on or turning off output current dampening,
d. Choosing a linear or logarithmic output.
2. Ranging the outputs means assigning values to the low (0 or 4 mA) and high (20 mA) outputs.
5.3.2 Definitions
1. CURRENT OUTPUTS. The analyzer provides either a continuous 4-20 mA or 0-20 mA output current directly
proportional to pH, ORP, redox potential, conductivity, resistivity, or TDS.
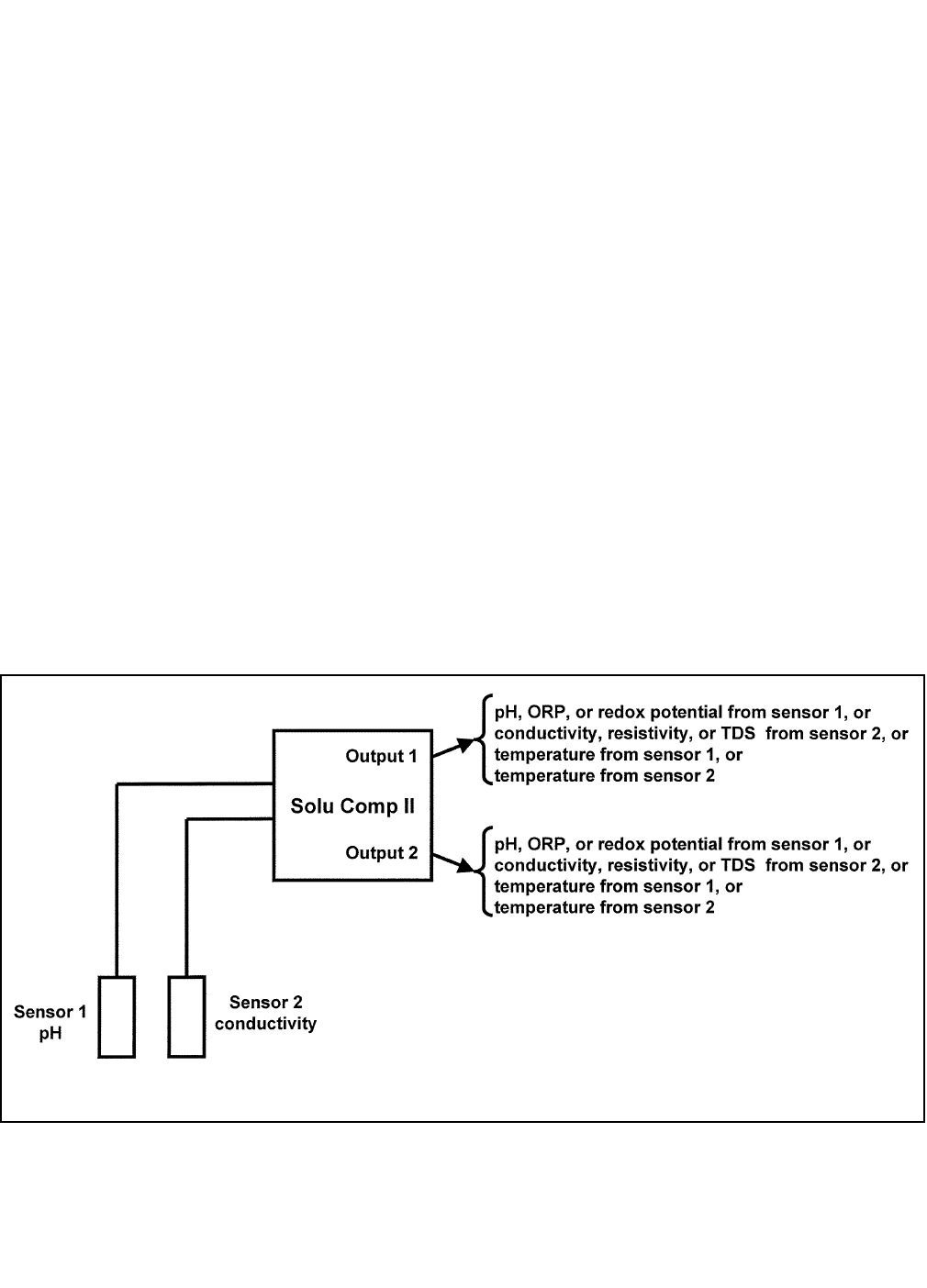
2. ASSIGNING OUTPUTS. Figure 5-1 shows the ways in which the outputs can be assigned.
3. DAMPEN. Output dampening smooths out noisy readings. It also increases the response time of the output.
With output dampening the time to reach 63% of final reading following a step change is 5 sec. Output damp-
ening does not affect the response time of the display.
4. MODE. The current output can be made directly proportional to the displayed value (linear mode) or directly
proportional to the common logarithm of the displayed value (log mode).
FIGURE 5-1. Assigning Outputs 1 and 2