272
FX3S/FX3G/FX3GC/FX3U/FX3UC Series
Programming Manual - Basic & Applied Instruction Edition
10 Arithmetic and Logical Operation (+, −, ×, ÷) – FNC 20 to FNC 29
10.1 FNC 20 – ADD / Addition
Related devices
1. Relationship between the flag operation and the sign (positive or negative) of a numeric value
→ For the flag operations, refer to Subsection 6.5.2.
Cautions
1. When using a 32-bit operation instruction (DADD or DADDP)
When specifying word devices, a 16-bit word device on the low-order side is specified first, and a word device with the
subsequent device number is automatically set for the high-order 16 bits.
To prevent number overlap, it is recommended to always specify an even number, for example.
2. When specifying the same device in the source and destination
The same device number can be specified for both the source and the destination.
In this case, note that the addition result changes in every operation cycle if a continuous operation type instruction
(ADD or DADD) is used.
Program example
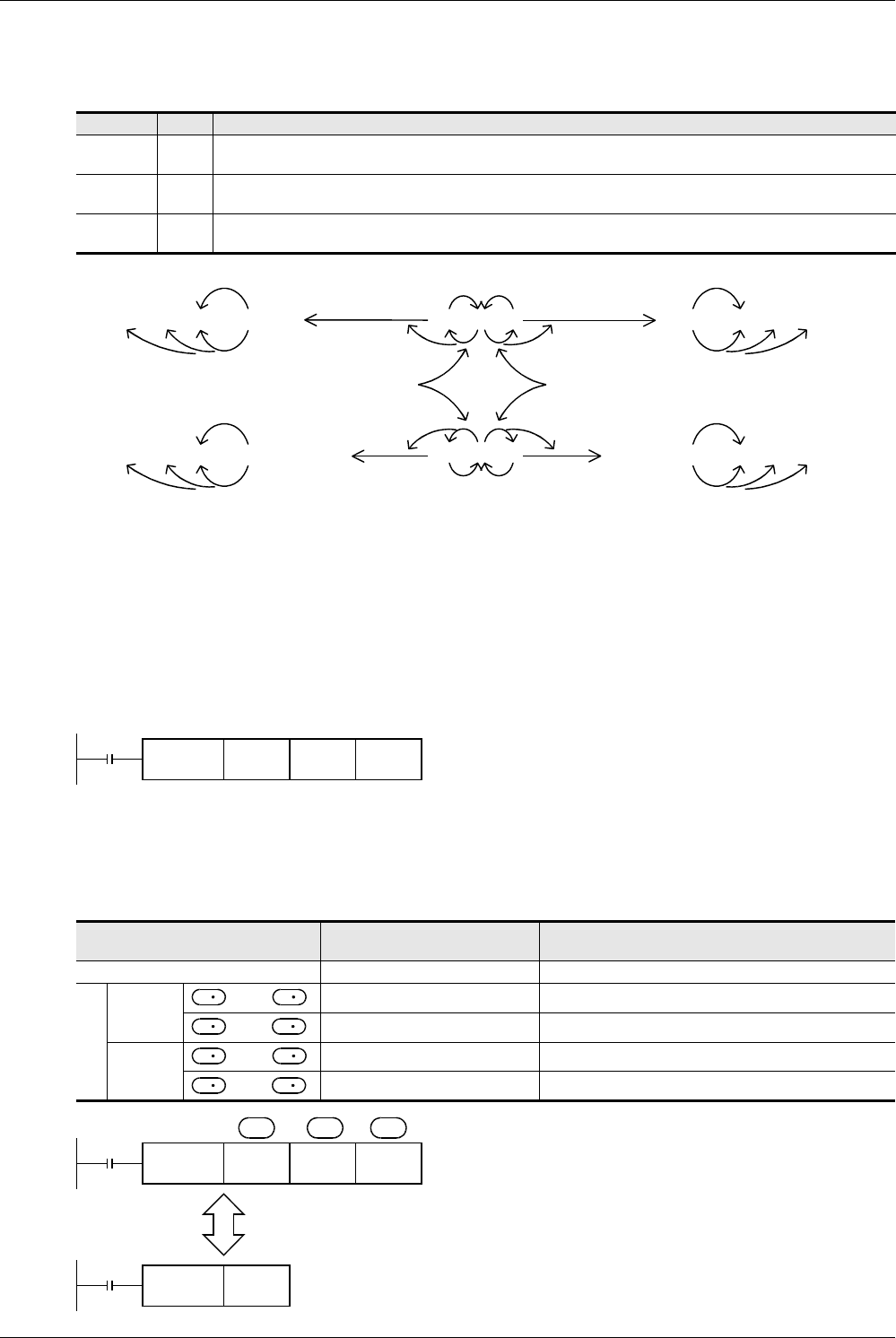
1. Difference between ADD instruction and INC instruction caused by a program for adding "+1"
When ADD[P] is executed, "1" is added to the contents of D0 every time X001 turns from OFF to ON.
ADD[P] instruction is similar to INCP instruction described later except the contents shown in the table below:
Device Name Description
M8020 Zero
ON : When the operation result is 0
OFF : When the operation result is not 0
M8021 Borrow
ON : When the operation result is less than −32768 (in 16-bit operation) or −2,147,483,648 (in 32-bit operation)
OFF :
When the operation result is not less than
−
32768 (in 16-bit operation) or
−
2,147,483,648 (in 32-bit operation)
M8022 Carry
ON : When the operation result is more than 32767 (in 16-bit operation) or 2,147,483,647 (in 32-bit operation)
OFF :
When the operation result is not more than 32767 (in 16-bit operation) or 2,147,483,647 (in 32-bit operation)
ADD, ADDP, DADD or DADDP
instruction
INC, INCP, DINC, DINCP instruction
Flag (zero, borrow or carry) Operates Does not operate
Operation result
16-bit
operation
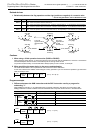
+(+1)=
+32767→0→+1→+2→ +32767→−32768→−32767
+(−1)=
←−2←−1←0←−32768 ⎯
32-bit
operation
+(+1)=
+2,147,483,647→0→+1→+2→ +2,147,483,647→−2,147,483,648→−2,147,483,647
+(−1)=
←−2←−1←0←−2,147,483,648 ⎯
Zero flag
−
2,
−
1, 0,
−
32768
Borrow flag
Zero flag
−
2,
−
1, 0,
−
2,147,483,648
Borrow flag
The most
significant bit of
data becomes
"1".
Zero flag
32767, 0, 1, 2
Carry flag
Zero flag
2,147,483,647, 0, 1, 2
Carry flag
Zero flag
−
1, 0, 1
Zero flag
−
1, 0, 1
The most
significant bit
of data
becomes "0".
FNC 20
ADD
D 0 K 25 D 0
X001
(D 0) + 25
→
(D 0)
S
D
S D
S
D
S D
FNC 20
ADDP
D 0 K 1 D 0
X001
(D 0) + 1
→
(D 0)
FNC 24
INCP
D 0
X001
(D 0) + 1
→
(D 0)
S
1
S
2
D