182
Chapter 19
Parameter Estimates
Figure 19-8
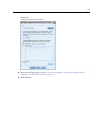
Parameter estimates
The parameter estimates show the effect of each predictor on Amount spent. The value of 5 18.249
for the i
ntercept term indicates that the grocery chain can expect a shopper with a family who uses
coupons from the newspaper and targeted mailings to spend $518.25, on average. You can tell
that the intercept is associated with these factor levels because those are the factor levels whose
paramet
ers are redundant.
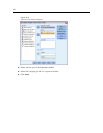
The sho
pfor coefficients suggest that among customers who use both mailed coupons and
newspaper coupons, those without family tend to spend less than those with spouses, who in
turn spend less than those with dependents at home. Since the tests of model effects showed
that th
is term contributes to the model, these differences are not due to chance.
The us
ecoup coefficients suggest that spending among customers with dependents at home
decreases with decreased coupon usage. There is a moderate amount of uncertainty in the
estimates, but the confidence intervals do not include 0.
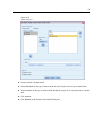
The interaction coefficients suggest that customers who do not use coupons or only clip from
the new
spaper and do not have dependents tend to spend more than you would otherwise
expect. If any portion of an interaction parameter is redundant, the interaction parameter is
redundant.
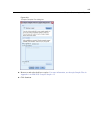
The deviation in the values of the design effects from 1 indicate that some of the standard
error
s computed for these parameter estimates are larger than those you would obtain if you
assumed that these observations came from a simple random sample, while others are smaller.
It is vitally important to incorporate the sampling design information in your analysis because
you mi
ght o therwise infer, for example, that the usecoup=3 coefficient is not different from 0!