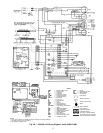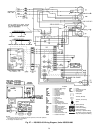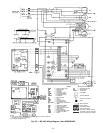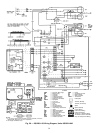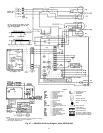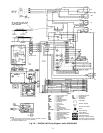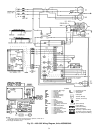
CHECKINGANDADJUSTING REFRIGERANT CHARGE
— The refrigerant system is fully charged with R-22 refrig-
erant, tested, and factory-sealed.
NOTE: Adjustment of the refrigerant charge is not required
unless the unit is suspected of not having the proper R-22
charge.
A superheat charging label is attached to the inside of the
compressor access door. The label includes a ‘‘Superheat Charg-
ing Table’’ and a ‘‘Required Suction-Tube (F) Temperature’’
chart.
An accurate superheat, thermocouple-, or thermistor-type
thermometer, a sling psychrometer, and a gage manifold are
required when using the superheat charging method for evalu-
ating the unit charge. Do not use mercury or small dial-type
thermometers because they are not adequate for this type of
measurement.
When evaluating the refrigerant charge, an indicated ad-
justment to the specified factory charge must always be
very minimal. If a substantial adjustment is indicated,
an abnormal condition exists somewhere in the cooling
system, such as insufficient airflow across either coil or
both coils.
Proceed as follows:
1. Remove caps from low- and high-pressure service
fittings.
2. Using hoses with valve core depressors, attach low- and
high-pressure gage hoses to low- and high-pressure serv-
ice fittings, respectively.
3. Start unit in cooling mode and let unit run until system
pressures stabilize.
4. Measure and record the following:
a. Outdoor ambient-air temperature (F db).
b. Evaporator inlet-air temperature (F wb).
c. Suction-tube temperature (F) at low-side service
fitting.
d. Suction (low-side) pressure (psig).
5. Using ‘‘Superheat Charging Table,’’compare outdoor-air
temperature (F db) with evaporator inlet-air temperature
(F wb) to determine desired system operating superheat
temperature. See Tables 8A-8H and 9A-9F.
6. Using ‘‘Required Suction-Tube (F) Temperature’’ table,
compare desired superheat temperature with suction (low-
side) operating pressure (psig) to determine proper suction-
tube temperature. See Table 10.
7. Compare actual suction-tube temperature with proper
suction-tube temperature. Using a tolerance of ± 3° F, add
refrigerant if actual temperature is more than 3° F higher
than proper suction-tube temperature, or remove refrig-
erant if actual temperature is more than 3° F lower than
required suction-tube temperature.
NOTE: If the problem causing the inaccurate readings is a
refrigerant leak, refer to Check for Refrigerant Leaks sec-
tion on page 23.
EVAPORATOR AIRFLOW AND AIRFLOW
ADJUSTMENTS
For cooling operation, the recommended airflow is 350
to 450 cfm for each 12,000 Btuh of rated cooling ca-
pacity. For heating operation, the airflow must produce
a temperature rise that falls within the range stamped on
the unit rating plate.
Table 6 shows the temperature rise at various airflow rates.
Tables 11-14 show both heating and cooling airflows at vari-
ous external static pressures. See Tables 15 and 16 for ICM
(Integrated Control Motor) units air delivery. Refer to these
tables to determine the airflow for the system being in-
stalled. See Table 17 for wet coil pressure drop.
NOTE: Be sure that all supply- and return-air grilles are open,
free from obstructions, and adjusted properly.
Shut off gas supply then disconnect electrical power to
the unit before changing blower speed. Electrical shock
can cause personal injury or death.
Airflow can be changed by changing the lead connections
of the blower motor.
Unit 48SS two- or 3-speed motors (except size 030) are
factory wired for low speed operation. Unit 48SS030 is fac-
tory wired for medium speed. Units 48SX024,036, and 048
(460 v) two- or 3-speed motors are factory wired for low
speed; units 48SX030 and 042 are factory wired for medium
speed.
For 208/230-v andA.O. Smith 460-v Blower Motors — The
motor leads are color-coded as follows:
3-SPEED 2-SPEED
black = high speed black = high speed
blue = medium speed red = low speed
red = low speed
To change the speed of the blower motor, remove the fan
motor speed leg lead from the blower relay (BR). This wire
is attached to terminal BM for single-phase and 3-phase units.
To change the speed, remove and replace with lead for de-
sired blower motor speed. Insulate the removed lead to avoid
contact with chassis parts.
For 460-v GE Motors — The motor leads are color coded as
follows:
3-SPEED 2-SPEED
black = high black = high
blue = jumper blue = jumper
orange = medium red = low
red = low
To change the speed of the blower motor, remove fan mo-
tor speed lead from the blower relay (BR) and replace with
the lead for the desired blower motor speed. The motor speed
lead is attached to terminal BM. Insulate removed lead end
to avoid contact with chassis parts. On 3-speed motors only,
connect orange lead to terminal BM of BR. To select high
speed on 460-v GE motors, separate the black (female QC)
from the blue lead (male QC) and connect the black lead to
the BR. Insulate the blue lead to avoid contact with any chas-
sis parts.
35