10
GBDFEINLPGRRUTRCZSVSLHGPO
10.2. Precautions concerning piping connec-
tion and valve operation
• Conduct piping connection and valve operation accurately.
• The gas side connecting pipe is assembled in the factory before shipment.
1 For brazing to the connecting pipe with flange, remove the connecting
pipe with flange from the valve, and braze it outside of the unit.
2 The refrigerant circuit is closed with a round, close-packed packing upon
shipment to prevent gas leak between flanges. As no operation can be
done under this state, be sure to replace the packing with the hollow pack-
ing attached at the piping connection.
3 At the mounting of the hollow packing, wipe off dust attached on the flange
sheet surface and the packing. Coat refrigerating machine oil (Ester oil,
ether oil or alkylbenzene [small amount]) onto both surfaces of the pack-
ing.
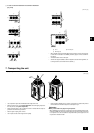
[Fig. 10.2.1]
A
E
D
C
B
• After evacuation and refrigerant charge, ensure that the handle is fully open. If
operating with the valve closed, abnormal pressure will be imparted to the
high- or low-pressure side of the refrigerant circuit, giving damage to the com-
pressor, four-way valve, etc.
• Determine the amount of additional refrigerant charge by using the formula,
and charge refrigerant additionally through the service port after completing
piping connection work.
• After completing work, tighten the service port and cap securely so as not to
generate any gas leakage.
• Flare machining dimension for systems using R410A is larger than that for
systems using other types of refrigerant in order to increase the air tightness.
• Refer to the table on the below for flare machining dimensions, and follow the
regulations set forth by the local authorities.
flare machining dimension (mm)
A Close-packed packing
B Hollow packing
C Valve
D Packing
E Connecting pipe with flange
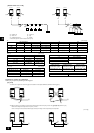
[Fig. 10.2.2]
<A> Valve
liquid side/
flared type
A
B
C
H
I
G
J
F
E
D
C
()
<B> Valve
gas side/
flanged type
()
<C> Valve
gas side/
flared type
()
outer diameter
ø6.35
ø9.52
ø12.7
ø15.88
ø19.05
size in inches
1/4"
3/8"
1/2"
5/8"
3/4"
dimension A
R410A
9.1
13.2
16.6
19.7
24.0
A
outer diameter
ø6.35
ø9.52
ø12.7
ø15.88
ø19.05
size in inches
1/4"
3/8"
1/2"
5/8"
3/4"
dimension B
R410A
17.0
22.0
26.0
29.0
36.0
B
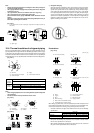
A Service port
For vacuuming in the refrigerant pipes on the site.
(Tightening torque 12 N·m [120 kg·cm])
B Shaft
Fully closed at the factory, when connecting the piping, and when vacuuming.
Open fully after these operations are completed.
<When opening>
• Turn the shaft counterclockwise with a hexagonal wrench.
• Turn around the shaft until it stops.
<When closing>
• Turn the shaft clockwise with a hexagonal wrench.
• Turn around the shaft until it stops.
C Flare nut
Coat the flare contact surface with refrigerating machine oil (small amount of
ester oil, ether oil, or alkyl benzene) and tighten the nut with a double-ended
wrench (refer to the following table for tightening torque).
D Cap
Remove the cap before operating the shaft. Be sure to return it to the original
position after completing the operation.
E Packing
Coat both sides of the packing with machine refrigerating oil (small amount of
ester oil, ether oil, or alkyl benzene) and tighten the flange.
(Tightening torque 25 N·m [250 kg·cm])
F Connecting pipe (accessory)
Be sure to remove the connecting pipe from the valve and braze it outside the unit.
G Field piping
Braze to the connecting pipe with unoxidized brazing.
H ø9.52 mm [3/8"] (PUHY-HP72, HP96, when combining PUHY-HP72, HP96)
ø12.7 mm [1/2"] (PUHY-HP72, HP96)
I ø22.2 mm [7/8"] (PUHY-HP96)
J ø19.05 mm [3/4"] (PUHY-HP72)
Appropriate tightening torque:
Appropriate tightening torque and its angle:
Warning:
When connecting a pipe to the service valve, be sure to use only the supplied
open-end flare nut, with small holes cut into the flats.
* Using a regular flare nut (i.e., non-supplied) will result in any water that
naturally flows into the nut being unable to escape.
Consequently, when the temperature becomes low, this water inside the nut
may freeze and cause damage to the joint. This, in turn, may result in a gas
leakage.
[Fig. 10.2.3]
Note:
If a torque wrench is not available, use the following method as a standard;
When you tighten the flare nut with a wrench, you will reach a point where
the tightening torque will abruptly increase. Turn the flare nut beyond this
point by the angle shown in the table above.
Outer diameter of
copper pipe (mm [in])
ø9.52 [3/8]
ø12.7 [1/2]
ø15.88 [5/8]
ø19.05 [3/4]
ø25.4 [1]
Shaft (N·m /kg·cm)
5/50
9/90
15/150
15/150
30/300
Size of hexagonal
wrench (mm)
4
4
6
6
10
Outer diameter of
copper pipe (mm [in])
ø9.52 [3/8]
ø12.7 [1/2]
ø15.88 [5/8]
ø19.05 [3/4]
Tightening torque
(N·m/kg·cm)
35 - 42/350 - 420
50 - 57.5/500 - 575
75 - 80/750 - 800
100 - 140/1000 - 1400
Tightening angle
(°)
60 to 90
30 to 60
20 to 35
flare nut size (mm)
Cap (N·m /kg·cm)
22/220
20/200
25/250
25/250
40/400